‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army represents one of the most sophisticated examples of digital political mobilization in India. It is an expansive, multi-layered network created under the broader umbrella of the Bharatiya Janata Party’s (BJP) IT Cell, designed to extend the party’s reach into every social and digital touchpoint where political influence can be cultivated. This initiative reflects a more profound shift from traditional campaign structures to data-driven, behavior-based digital persuasion, combining centralized message control with localized community activation.
Origins and Strategic Intent
The concept of ‘Modi Mitra’ (translated as “Friends of Modi”) emerged as part of the BJP’s strategy to transform supporters into digital volunteers who amplify the Prime Minister’s message through social media, WhatsApp, and hyperlocal digital forums. The initiative is rooted in the BJP’s belief that modern elections are not won merely through physical rallies or advertisements but through continuous digital engagement that maintains emotional resonance between the leader and citizens.
By design, this digital army acts as both a propaganda amplifier and a real-time feedback mechanism, ensuring that public sentiment is monitored, narratives are shaped, and political messaging evolves dynamically.
Structure and Hierarchical Coordination
At the organizational level, the ‘Modi Mitra’ ecosystem is managed by the BJP’s national IT and social media departments, coordinated through state and district-level digital conveners. The model mirrors a military command chain, where national content such as videos, infographics, hashtags, and talking points is distributed via encrypted channels, including WhatsApp broadcast groups and internal platforms.
Local ‘Modi Mitras’ often include grassroots workers, youth volunteers, or social media enthusiasts, who then contextualize these messages in regional languages, dialects, and cultural idioms to fit their community’s sentiments. This creates a cascading communication pyramid that ensures the same ideological message is delivered with localized authenticity and emotional relevance.
Data-Driven Micro-Targeting
A defining feature of the ‘Modi Mitra’ model is its heavy reliance on micro-targeted outreach powered by data analytics and psychographic profiling. The IT Cell reportedly integrates voter data from multiple sources, including booth-level surveys, electoral rolls, social media engagement metrics, and sentiment analyses, to create granular audience segments.
Each segment from first-time voters to urban professionals and rural women beneficiaries receives tailored content that aligns with their aspirations, fears, and digital behavior patterns. Campaigns are optimized through A/B testing, machine learning algorithms, and geo-tagged engagement data, allowing precise adjustments in tone, timing, and platform usage.
Digital Infrastructure and Tools
The network leverages a robust suite of digital tools. Proprietary BJP apps, such as NaMo App and BJP4India, serve as central repositories for campaign material, updates, and volunteer coordination. Automated bots and data dashboards track metrics like post engagement, volunteer activity, and issue traction in real time.
The system’s backbone lies in WhatsApp clusters, which serve as decentralized information hubs. Each ‘Modi Mitra’ typically manages several local WhatsApp groups, ensuring that official narratives penetrate even semi-urban and rural constituencies beyond the reach of mainstream media. Simultaneously, AI-assisted moderation filters content flow, detects dissent, and enhances message consistency.
Psychological and Emotional Framing
The campaign’s messaging strategy integrates emotional storytelling and narratives of national identity, portraying Modi as a reformer, protector, and visionary leader. Digital creatives employ motifs of nationalism, self-reliance, and cultural pride, often mixing personal success stories with government achievements to evoke trust and admiration.
‘Modi Mitras’ are trained to use relatable local anecdotes, humor, and micro-influencer techniques to foster organic engagement rather than overt political propaganda. This emotional personalization helps bypass political fatigue and increases shareability across family and community groups.
Counter-Narrative and Information Control
Beyond promotion, the digital army serves as a defensive mechanism against opposition attacks, misinformation, and negative press. The IT Cell uses rapid response teams to monitor trending topics, deploy coordinated counter-hashtags, and flood timelines with pro-BJP narratives. Fact-checking cells work in parallel to neutralize anti-BJP content. At the same time, volunteers are encouraged to “correct” misinformation within their networks, turning each supporter into a micro-influencer and message guardian.
Ethical and Regulatory Concerns
While effective, the ‘Modi Mitra’ system has sparked ethical debates around privacy, data exploitation, and the manipulation of online discourse. Critics argue that psychographic targeting blurs the line between legitimate outreach and behavioral manipulation, especially in the absence of a comprehensive data protection law in India.
Blurred boundaries between the party’s official communication and citizen volunteerism raise questions about accountability, misinformation, and echo-chamber effects. Nevertheless, the BJP’s model has been studied globally as a benchmark in digital grassroots political engineering.
Electoral Impact and Evolution
The digital army’s influence was visible in successive elections from the 2014 and 2019 Lok Sabha campaigns to state elections in Uttar Pradesh, Gujarat, and Karnataka. Its scalability, speed, and narrative consistency have given the BJP a permanent campaign advantage, enabling 24/7 engagement rather than election-season mobilization.
Recent iterations have expanded into AI-powered sentiment prediction, influencer collaborations, and digital listening centers, signaling a transition toward an even more automated, predictive model of political communication.
Digital Army Deployment: From National IT Cell to Booth-Level Targeting
The ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army showcases how the BJP transformed digital engagement into a grassroots political weapon. Managed by the national IT Cell and coordinated through state and district-level networks, this system enables message dissemination and micro-targeted outreach down to the booth level.
Using data analytics, psychographic profiling, and AI-assisted tools, volunteers tailor messages in regional languages that reflect local issues and emotions. This digital army ensures ideological consistency while personalizing content for every demographic segment, creating a seamless link between centralized strategy and neighborhood-level influence.
Centralized Command and Strategic Control
The Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) has built a structured digital communication system that operates from the national level down to the smallest voting unit. The National IT Cell serves as the command center for this operation. It manages the creation, coordination, and delivery of digital campaigns while ensuring ideological consistency across states.
Teams within the IT Cell analyze data, identify voter clusters, and create tailored communication materials such as short videos, social media graphics, and local narratives. Once finalized, this content flows through secure digital channels to state and district-level coordinators who handle local adaptation.
The goal is simple: build a continuous feedback loop where data from the ground shapes future messaging. Every volunteer, whether a senior strategist or a booth-level worker, participates in this cycle. The system relies on centralized analytics but depends on localized human networks for contextual delivery.
State and District-Level Coordination
At the next level, digital conveners in each state act as intermediaries between the national IT Cell and the booth-level volunteers. They oversee regional adaptations, translation of campaign materials, and timing of releases across platforms such as WhatsApp, Facebook, and X (formerly Twitter). State teams monitor how content performs regionally and report back on trends, sentiment shifts, and opposition narratives.
District-level coordinators break this structure further into smaller units that align with assembly constituencies. Their task is to identify influential digital voices, community leaders, and local media outlets that can amplify the BJP’s communication strategy. This structure allows digital messaging to align with local priorities such as welfare programs, infrastructure updates, or community issues while maintaining national coherence.
Booth-Level Execution and Volunteer Networks
The true operational strength of the BJP’s digital system lies at the booth level. Each booth typically covers around 1,000 voters. Volunteers known as “Modi Mitras” or “Booth IT Karyakartas” work as the last link in the digital chain. They share curated content within their personal and community WhatsApp groups, participate in issue-based discussions, and counter misinformation in real time.
These volunteers personalize messages for their neighborhoods, using local dialects and relatable examples. For instance, a national welfare scheme might be explained through the story of a beneficiary in that particular area. This grassroots customization gives the campaign authenticity and helps sustain digital conversations between elections, not just during campaigns.
Data and Micro-Targeting Infrastructure
The digital army operates on a data-driven model. Information from electoral rolls, field surveys, and digital engagement metrics feeds into a centralized database. Machine learning tools analyze this data to identify potential voters and categorize them based on demographics, profession, interests, and online behavior.
Targeted outreach campaigns then deliver messages tailored to these segments. Young voters receive aspirational and development-focused narratives on Instagram or YouTube Shorts, while older demographics receive updates on welfare programs via WhatsApp messages. Booth-level data updates ensure every volunteer understands the political mood in their assigned area, allowing for real-time content calibration.
Information Flow and Command Hierarchy
Information travels in both directions. The IT Cell provides standardized content and talking points to maintain message discipline, while local teams send feedback about reactions, misinformation trends, and opposition strategies. This exchange ensures the central team can quickly modify narratives.
Weekly digital briefings and coordination calls reinforce uniform messaging. All content undergoes vetting before public release, ensuring factual consistency and alignment with the overall campaign strategy. The system’s efficiency depends on precise coordination, accountability, and rapid communication within this hierarchy.
Tools, Platforms, and Monitoring
The BJP uses a combination of proprietary and public digital tools to manage its communication. The NaMo App acts as a hub for official content, campaign updates, and volunteer coordination. The BJP4India platform serves a similar purpose at the state level. WhatsApp remains the most influential communication medium because of its reach in semi-urban and rural areas.
AI-assisted dashboards track engagement rates, post-performance metrics, and sentiment shifts across digital channels. These insights help regional teams adjust timing, format, or tone based on user responses. In many areas, digital war rooms operate during elections to monitor narrative flow, coordinate counter-responses, and deploy volunteers to handle online controversies or misinformation spikes.
Psychological Framing and Narrative Adaptation
Messaging across this digital structure follows clear thematic lines: national pride, development, leadership credibility, and welfare success stories. Each volunteer is trained to present information not as propaganda but as community dialogue. They use anecdotes, humor, and relatable examples to reinforce loyalty and reduce political fatigue.
Local storytelling plays a central role. For example, a policy announcement might be localized through neighborhood testimonials, making it emotionally relevant. The combination of emotional appeal and social proof increases message retention and trust among undecided voters.
Ethical and Operational Implications
This level of digital precision brings both advantages and challenges. On one hand, it democratizes participation, allowing ordinary citizens to become part of a coordinated national campaign. On the other hand, it raises concerns about privacy, misinformation, and manipulation. The extensive use of personal data for psychographic profiling has drawn scrutiny from policy experts and data ethics researchers.
Transparency in data sourcing and accountability in message creation remain pressing issues. Without regulatory oversight, micro-targeting can blur the line between persuasion and behavioral engineering. Balancing campaign efficiency with ethical boundaries is therefore essential for maintaining public trust.
Continuous Campaigning and Impact
The digital army does not dissolve after elections. It remains active year-round to sustain engagement, counter criticism, and highlight ongoing government initiatives. This perpetual campaigning model keeps the BJP’s message visible in daily online conversations. The strategy has contributed significantly to the party’s dominance across multiple electoral cycles by turning digital networks into permanent political infrastructure.
Best Ways of ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army
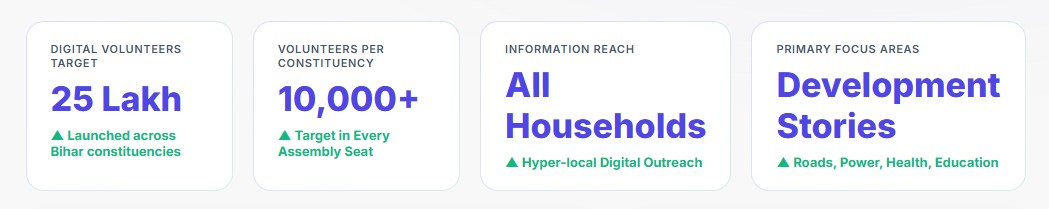
The most effective aspects of the ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army lie in its structured digital hierarchy, real-time voter engagement, and data-driven outreach. The network integrates over 150,000 trained social media workers and 5 million WhatsApp groups to amplify the BJP’s message from the national to the booth level.
Its success comes from using pre-approved localized content, regional influencers, and targeted voter data from the Sakal App. With strong operational discipline, multilingual content production, and secure digital coordination, the Digital Army ensures consistent, personalized communication that reaches deep into India’s electoral landscape.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Digital Structure | The Modi Mitra Digital Army follows a well-defined hierarchy connecting the BJP’s National IT Cell to state, district, and booth-level teams for synchronized communication and execution. |
| Voter Engagement | The network operates through over 5 million WhatsApp groups and localized social media accounts, ensuring direct, real-time interaction with voters across regions. |
| Content Strategy | About 80% of content is pre-approved and centrally produced in Delhi, while regional teams adapt it into local languages and formats to improve cultural relevance. |
| Influencer Integration | More than 100 regional influencers per campaign target amplify party messages through paid and unpaid collaborations, increasing reach among youth and digital audiences. |
| Data-Driven Targeting | The Sakal App supports voter segmentation and micro-targeting based on caste, religion, and regional demographics, enabling precision-level outreach strategies. |
| Regional Localization | Local-language content production and culturally tuned messaging strengthen connections with regional audiences and enhance message authenticity. |
| Operational Efficiency | Booth-level volunteers distribute 5–10 posts daily, combining digital and on-ground efforts for maximum consistency and message reach. |
| Security & Compliance | All digital operations follow strict content approval, voter data protection, and platform compliance policies to maintain credibility and prevent misuse. |
| Performance Metrics | Engagement rates range between 12–25%, with influencer collaborations boosting visibility by 40–60% and conversion campaigns achieving up to 32% registration success. |
| Strategic Coordination | The Modi Mitra App enables two-way communication between national and regional units, ensuring rapid response, consistent messaging, and data-backed decision-making. |
National Command
The National IT Cell serves as the strategic core of the ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army, overseeing digital communication, analytics, and content coordination across India. It designs and distributes campaign material, manages volunteer databases, and monitors voter sentiment through centralized data systems.
By combining technology, message control, and real-time analytics, the national command ensures that every digital action from a tweet to a booth-level WhatsApp message supports a unified political narrative. This centralized leadership maintains consistency, speed, and discipline across the party’s vast digital network.
BJP IT Cell National HQ
The BJP IT Cell National Headquarters functions as the operational and analytical hub of the party’s digital ecosystem. It develops campaign strategies, designs data-driven communication models, and supervises regional digital teams to ensure uniformity in messaging.
The HQ integrates voter data, social media analytics, and sentiment insights to craft precise narratives distributed through state and district coordinators. Acting as both a control center and innovation lab, it maintains message discipline, monitors engagement in real time, and directs the digital army’s coordinated outreach from the national to the booth level.
Centralized Digital Command
The BJP IT Cell National Headquarters operates as the strategic control center for the party’s digital and communication operations. It coordinates over 150,000 national programs that connect central leadership with state, district, and booth-level units.
These programs range from online campaigns and policy communication to digital outreach and public engagement initiatives. The headquarters oversees data analysis, content production, and real-time sentiment tracking, ensuring every campaign reflects the party’s strategic objectives and public narrative.
Volunteer and Network Coordination
The headquarters manages a large digital volunteer base of more than 2.5 million members, collectively referred to as the “Modi Mitra Digital Army.” These volunteers are the operational strength of the BJP’s online communication framework.
The IT Cell provides them with structured content, verified information, and daily communication guidelines. Volunteers are organized by state and constituency to maintain regional accuracy and consistency. Through centralized coordination, the national HQ converts digital supporters into active campaign participants who amplify the party’s messaging across social and community networks.
Modi Mitra App Network
The Modi Mitra App is a key platform connecting the national HQ to its vast digital army. It distributes campaign materials, multimedia assets, and instructions directly from the center to volunteers. The app also collects engagement metrics, field updates, and volunteer activity data.
This feedback loop helps the IT Cell evaluate participation, message reach, and regional effectiveness. The platform standardizes messaging across all levels, ensuring every digital post, share, or comment aligns with official communication goals.
WhatsApp Communication System
At the foundation of this network lies an extensive system of more than 5 million WhatsApp groups, coordinated hierarchically. Each group acts as a micro-channel for local mobilization, event updates, and rapid information exchange. The IT Cell monitors activity through analytics dashboards that track engagement patterns and flag misinformation.
This allows the HQ to respond swiftly, circulate clarifications, and fine-tune messaging for different regions. The WhatsApp structure enables real-time, two-way communication between national leaders and local supporters, extending digital reach even into the smallest constituencies.
Data Intelligence and Real-Time Adaptation
The headquarters integrates analytics, AI-assisted monitoring, and feedback from the Modi Mitra App and WhatsApp networks to guide decisions. It studies voter behavior, topic trends, and engagement sentiment to identify what resonates with specific demographics.
Regional coordinators use this data to localize campaign messages while maintaining alignment with the national narrative. Real-time intelligence ensures the BJP’s communication stays adaptive, timely, and consistent across multiple states and audiences.
Strategic Purpose and Impact
The BJP IT Cell National HQ represents a scalable model of digital political organization that combines structure, analytics, and participation. By managing 150,000+ programs, mobilizing 2.5 million volunteers, and operating through 5 million WhatsApp groups supported by the Modi Mitra App, it creates a unified system that merges top-down strategy with bottom-up participation.
This digital infrastructure allows the party to maintain continuous engagement with citizens, shape public opinion effectively, and sustain a high level of message control across India’s political and social landscape.
Regional Operations
Regional operations form the connective layer between the BJP’s National IT Cell and its booth-level digital teams. State and district-level coordinators manage the translation, adaptation, and timing of campaign messages to suit regional contexts and local sentiments.
They oversee digital volunteers, track social media engagement, and gather on-the-ground feedback to update he central strategy. These teams ensure that national narratives are communicated in local languages with cultural relevance, maintaining ideological consistency while addressing region-specific priorities.
Through this structure, the BJP’s digital network achieves both precision and scale in outreach.
Regional IT Deployment
Regional IT Deployment ensures that the BJP’s digital strategy reaches every state, district, and constituency with operational precision. Regional IT teams act as the implementation arm of the National IT Cell, adapting centrally created content to reflect local issues, dialects, and voter interests.
They manage digital war rooms, monitor social media trends, and coordinate thousands of volunteers through the Modi Mitra App and WhatsApp groups. By combining data analytics with localized communication, these teams convert national directives into region-specific campaigns that strengthen booth-level engagement and maintain message discipline across all digital fronts.
Scalable Digital Operations
Regional IT Deployment serves as the operational bridge between the BJP’s National IT Cell and its on-the-ground digital units. Each regional team is responsible for executing the party’s data-driven outreach strategy within its designated states and constituencies.
The system is structured to achieve a target of engaging 2.5 million voters per constituency, ensuring that national campaigns are translated into local-level communication. Regional IT cells monitor digital activity, manage volunteer databases, and adapt central messages to fit the cultural, linguistic, and political dynamics of their respective regions.
Volunteer Mobilization and Target Management
To sustain large-scale outreach, regional teams coordinate with local digital conveners to recruit, train, and manage volunteers. The 2.5 million target per constituency reflects the BJP’s focus on measurable engagement rather than generic outreach.
Each volunteer is assigned specific communication goals such as managing WhatsApp groups, moderating digital discussions, or reporting feedback through the Modi Mitra App. This approach allows regional teams to track participation rates and maintain accountability across all layers of the digital network.
Missed Call Registration System
A key recruitment and verification tool within the regional structure is the Missed Call Registration system. This system enables citizens to register as “Modi Mitras” by giving a missed call to a dedicated number. Once registered, the individual’s contact is added to a verified database, linking them directly to the nearest regional IT cell.
The system ensures quick and authenticated volunteer onboarding without requiring extensive documentation. It also supports segmentation, enabling teams to categorize participants by geography, demographics, and online activity for targeted engagement.
Instant Onboarding and Integration
The Instant Onboarding process connects new volunteers to the BJP’s digital ecosystem within minutes. After registration, each volunteer receives an automated message with instructions to download the Modi Mitra App and join regional WhatsApp groups.
Through these channels, volunteers gain access to training materials, official campaign content, and task assignments. This seamless integration minimizes administrative delays and allows rapid mobilization during campaign cycles or issue-based drives.
Regional Monitoring and Data Synchronization
Regional IT teams maintain dashboards that track registrations, volunteer activity, and engagement performance. Data from the Modi Mitra App and WhatsApp networks flows back to the regional control centers, allowing real-time analysis of participation rates, message reach, and sentiment trends. Coordinators review these insights weekly and forward summary reports to the National IT Cell for further strategy refinement. This closed feedback loop ensures that digital efforts remain consistent, responsive, and data-driven.
Strategic Impact
Regional IT Deployment converts national directives into localized, measurable action. By integrating the Missed Call Registration system, instant onboarding tools, and structured engagement targets, the BJP ensures precision in volunteer management and message distribution.
Each regional cell operates like a digital command post, monitoring participation, adapting narratives, and keeping the party’s communication synchronized from headquarters to the grassroots.
Regional Content Coordination
Regional Content Coordination ensures that the BJP’s national digital messaging is localized for each state and constituency. Regional IT teams adapt centrally prepared materials videos, infographics, and slogans to local languages and dialects, aligning them with regional issues, festivals, and public sentiment.
They collaborate with district and booth-level volunteers to distribute this content through the Modi Mitra App and WhatsApp groups. This structure maintains message consistency while ensuring cultural relevance, allowing national narratives to resonate authentically at the grassroots level and sustain continuous voter engagement.
Localized Messaging and Video Production
Regional Content Coordination focuses on translating the BJP’s national communication strategy into locally relevant formats. Each regional IT cell is responsible for local language video production, ensuring that national themes are communicated in a tone and style familiar to state audiences.
Teams create short videos, reels, and testimonials using regional languages and cultural references to make digital campaigns relatable. These videos often highlight local achievements, welfare programs, and interactions with leaders to strengthen emotional connections with voters.
Structured Content Pipeline from Delhi HQ
Nearly 80 percent of digital content is pre-planned and produced by the Delhi Headquarters, where specialized teams handle messaging, design, and video direction. Once finalized, this content is distributed to regional teams for adaptation.
The Delhi HQ ensures that all media align with the central narrative, maintaining ideological consistency and message discipline across platforms. The remaining 20 percent of content is region-specific, created by state units to respond to local developments, opposition narratives, or emerging social issues.
Coordination between Central and Regional Teams
The Delhi HQ and regional IT units operate in constant coordination through a structured workflow. Central teams share raw footage, campaign guidelines, and templates, while regional teams modify them with local visuals, language overlays, and subtitles.
Daily video conferences and content review calls help maintain uniformity while allowing room for local creativity. This system ensures that all digital assets from national campaigns to booth-level videos reflect the same strategy, tone, and data-backed messaging.
Integration with Modi Mitra and WhatsApp Networks
Once approved, localized content flows through the Modi Mitra App and regional WhatsApp groups, where volunteers distribute it to targeted voter segments. This networked distribution model ensures that the right message reaches the right audience at the right time.
Regional teams track engagement levels and report performance metrics back to Delhi HQ for analysis. Continuous data exchange between headquarters and regional offices helps refine future campaigns and identify content types that generate the highest response rates. rates
Efficiency and Real-Time Adaptation
Because 80 percent of content is pre-produced, regional teams can deploy materials quickly without waiting for approval cycles. The Delhi HQ provides real-time guidance for the remaining adaptive content, especially during major events, speeches, or election campaigns.
Regional video units use mobile production setups to capture live footage and integrate it into ongoing campaigns. This hybrid model, combining central planning with localized execution, enables fast, controlled, and context-sensitive communication.
Strategic Purpose
Regional Content Coordination ensures that the BJP’s digital communication remains both consistent and adaptive. The Delhi HQ defines the national message, while regional teams translate it into culturally accurate, language-specific narratives.
The combination of local language production, pre-planned content, and central oversight builds a scalable digital communication system that preserves ideological integrity while amplifying regional relevance. This structure allows the Modi Mitra Digital Army to sustain continuous engagement across India’s linguistic and social diversity with efficiency and precision.
Hyperlocal Booth-Level Operations
Hyperlocal Booth-Level Operations form the foundation of the BJP’s ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army, connecting national digital strategy directly to neighborhood-level engagement. Each booth covers around 1,000 voters and is managed by trained volunteers who share verified content through WhatsApp groups, local meetings, and the Modi Mitra App.
These volunteers personalize national messages into local dialects, highlight regional issues, and collect voter feedback for higher-level analysis. This structure transforms every booth into a digital communication hub, ensuring real-time coordination, message consistency, and community-level political mobilization.
Structure and Local Engagement
Hyperlocal Booth-Level Operations form the most granular layer of the BJP’s digital communication system under the ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army. Each booth represents a defined geographic unit covering roughly 1,000 voters and is managed by a small digital team of trained volunteers.
These teams execute targeted outreach by sharing verified content, collecting feedback, and tracking public sentiment through WhatsApp groups and the Modi Mitra App. Booth-level operations ensure that national and regional narratives are translated into local dialects and reach individual households directly. This model strengthens voter relationships and enables data-backed political communication at the grassroots level.
Regional Data Enrichment
A critical function of booth-level teams is regional data enrichment. Volunteers continuously update demographic, voter, and issue-based data collected from field interactions, surveys, and digital engagement. This information flows upward to district and regional IT cells, improving the accuracy of voter segmentation and content targeting.
By combining local insights with analytics from the central database, the system refines audience profiles and enhances micro-targeting precision. Regional data enrichment also identifies emerging concerns or shifts in voter sentiment, allowing for quick message recalibration.
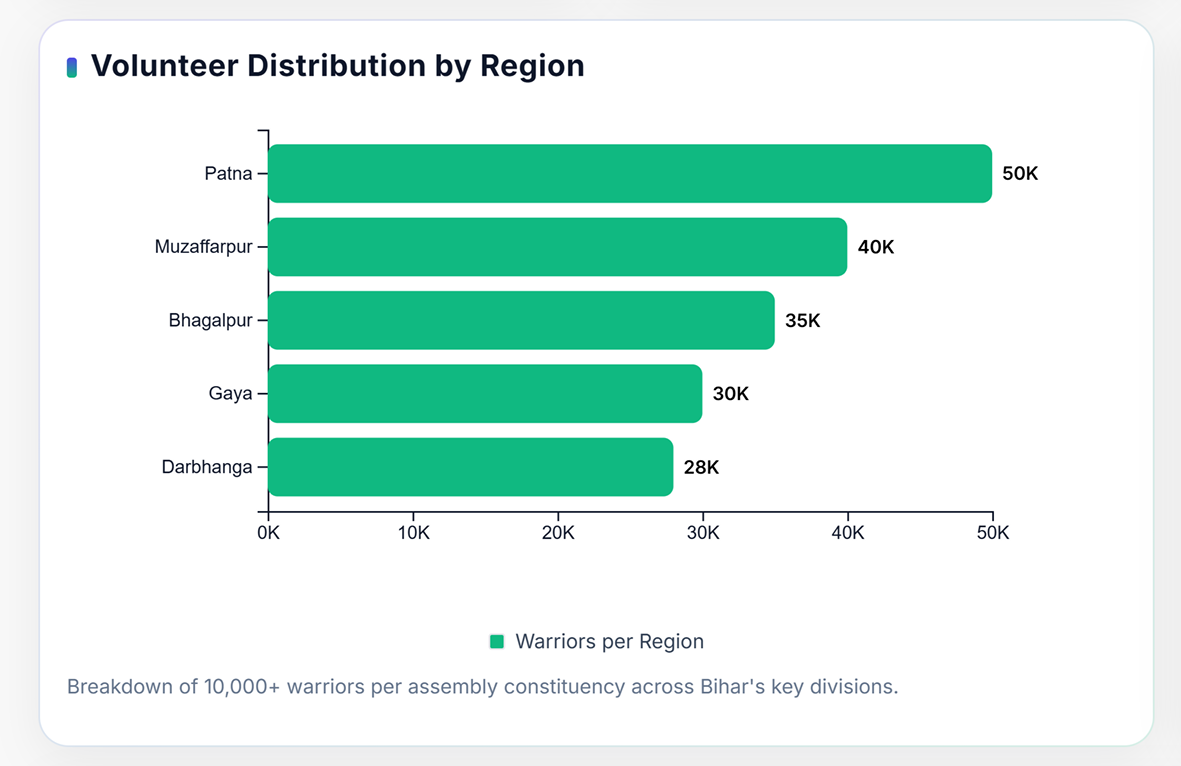
Volunteer Recruitment and 5,000+ Member Entry
Each constituency maintains a target of 5,000 or more active booth-level members responsible for digital outreach and data collection. Recruitment primarily occurs through missed-call registrations, community referrals, and Modi Mitra App sign-ups. New members undergo instant onboarding and receive standardized training on message delivery, data entry, and online behavior guidelines.
Once integrated, they become part of the local communication chain and participate in both digital and offline voter engagement drives. This extensive volunteer network ensures that every booth operates as a functioning digital unit capable of two-way communication between citizens and party command structures.
Real-Time Communication and Feedback Loops
Booth-level volunteers maintain direct contact with regional coordinators, sharing performance metrics and voter responses through app-based dashboards. Feedback is categorized into sentiment trends, issue reports, and outreach effectiveness.
This continuous data flow enables regional teams to make evidence-based adjustments to content strategy and voter targeting. The result is a tightly controlled communication structure that adapts quickly to local dynamics while maintaining the central message.
Strategic Impact
The integration of hyperlocal operations, regional data enrichment, and a large volunteer base transforms the BJP’s digital outreach into a highly adaptive ecosystem. Each booth functions as both a communication hub and a data node, feeding information to higher levels while ensuring every voter receives personalized engagement. The structure’s scalability and precision allow the party to maintain real-time awareness of ground realities, strengthen its digital presence, and build sustained political influence at the community level.
Hierarchical Groups
Hierarchical Groups form the communication backbone of the BJP’s ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army, linking the National IT Cell with millions of volunteers across states, districts, and booths. Each layer follows a structured command chain, national, regional, district, and booth-level lensuring that official content flows seamlessly downward while feedback moves upward in real time.
This structure allows consistent message delivery, quick coordination, and precise monitoring of engagement across 5 million WhatsApp groups and the Modi Mitra App network. By maintaining this disciplined hierarchy, the BJP ensures centralized control with localized adaptability throughout its digital outreach system.
National-to-Booth Communication Chain
The BJP’s ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army operates through a structured hierarchy that connects the National IT Cell directly to local-level volunteers. This network operates vertically from national to booth-level groups, ensuring a controlled, consistent flow of information.
Central directives, campaign materials, and verified updates are issued from the national command center and distributed sequentially through state, district, and constituency-level groups before reaching the booth-level volunteers. This organized chain allows synchronized messaging across digital platforms and ensures that communication remains both fast and traceable.
Regional Deployment and Group Distribution
In states like Himachal Pradesh, the hierarchical structure includes over 8,000 active WhatsApp groups, with one group dedicated to each booth. Each group operates under the guidance of district-level coordinators who oversee message distribution and activity tracking.
Regional administrators monitor engagement data, flag misinformation, and report participation metrics back to the state and national teams. This state-specific model helps maintain uniform communication standards while allowing local teams to adjust tone and language according to regional contexts.
Local Coordination: The Mandi Model
The Mandi town network exemplifies the granular execution of this hierarchy. It maintains over 400 dedicated WhatsApp groups managed by approximately 500 trained volunteers. Each volunteer is assigned to a specific booth or neighborhood group and is responsible for sharing approved content, gathering community feedback, and reporting voter sentiment.
These volunteers function as both digital communicators and field-level informants, linking online narratives with offline realities. The Mandi model highlights how the hierarchical system can operate efficiently even in smaller towns by leveraging tight coordination and clearly defined responsibilities.
Oversight and Feedback Mechanism
Each tier within the hierarchy plays a distinct role. National and state-level groups control narrative consistency, while district and booth-level groups handle regional dissemination and citizen interaction. Feedback from local volunteers flows up through the same structure, enabling leadership to analyze responses, adjust messaging, and address local issues promptly.
Daily reports on engagement, reach, and responsiveness are compiled by regional teams and reviewed at the state command centers before being shared with the National IT Cell.
Strategic Function and Impact
This hierarchical model combines centralized control with localized adaptability. It ensures that digital communication remains uniform in message but flexible in expression. With thousands of regional and booth-level groups, including the Himachal and Mandi networks, the BJP has built a scalable digital infrastructure capable of real-time mobilization and targeted outreach.
Every group function as a micro-unit of influence, reinforcing national narratives while maintaining local relevance. This disciplined digital framework allows the party to manage millions of interactions simultaneously, sustaining constant visibility and engagement across India’s political landscape.
Micro-Targeted Demographics
Micro-Targeted Demographics define the data-driven outreach model of the BJP’s ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army. Using voter databases, social media analytics, and behavioral insights, the IT Cell segments audiences by age, gender, location, occupation, religion, and digital behavior.
Each segment receives tailored messages that reflect their interests and priorities. Youth get development-oriented content, women receive welfare-related updates, and professionals see governance and policy achievements.
This targeted communication, distributed through the Modi Mitra App and WhatsApp networks, ensures high engagement and emotional resonance, allowing the BJP to maintain personalized voter relationships across every constituency.
Data-Driven Voter Segmentation
The BJP’s ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army uses a data-centric approach to segment and target voters across caste, religion, geography, and social behavior. Each IT Cell team analyzes demographic data, digital engagement, and electoral history to identify key voter clusters.
Messages are customized to resonate with specific communities and issues relevant to them. This form of segmentation enables precision targeting and ensures that every voter group receives content that aligns with its cultural identity and social priorities.
Caste and Religion-Based Outreach
Caste and religion remain central to the BJP’s digital mobilization strategy. Regional IT teams design communication frameworks that address the aspirations, beliefs, and sensitivities of various communities. For example, campaigns tailored for OBC, Dalit, and minority groups highlight inclusion policies, welfare initiatives, and cultural respect.
Religious outreach focuses on reinforcing narratives of faith, heritage, and social unity while maintaining ideological coherence. This micro-targeting model uses data and cultural cues to deepen voter trust and sustain long-term engagement.
Uttar Pradesh Digital Network
In Uttar Pradesh, one of India’s most politically influential states, the scale of this micro-targeting is extensive. Each IT Cell manages approximately 163,000 members, divided across constituencies to ensure coverage at the booth level.
These members are trained to identify voter sentiments, distribute personalized digital material, and track response rates. Uttar Pradesh’s size and diversity make it a testing ground for refining segmentation models that combine caste, religion, and regional dynamics within the digital network.
Maharashtra Urban Booth Focus
In Maharashtra, the strategy emphasizes urban booth-level operations to strengthen influence among working professionals, students, and the urban middle class. The BJP’s IT teams focus on high-density urban clusters such as Mumbai, Pune, and Nagpur, where digital engagement rates are higher.
Each booth operates as a micro-unit focusing on community concerns such as infrastructure, entrepreneurship, and public safety. The urban focus allows the digital army to link governance achievements to voters’ daily experiences, increasing credibility and digital reach.
Localized Message Content
The success of micro-targeting depends on the ability to craft localized message content that reflects regional dialects, socio-economic conditions, and local priorities. Regional teams translate national campaign material into vernacular languages and infuse it with local examples, cultural references, and testimonials.
This process gives every piece of content contextual relevance while maintaining consistency with the national narrative. The combination of cultural adaptation and data analytics ensures that communication feels personal rather than generic.
Strategic Impact
The micro-targeted demographic model allows the BJP to merge a large-scale organization with individual-level precision. In states like Uttar Pradesh and Maharashtra, it combines demographic segmentation with localized communication to sustain continuous engagement.
Each volunteer and booth network operates within defined demographic boundaries, ensuring maximum efficiency in outreach. This structure transforms digital campaigning from mass communication into direct voter interaction, reinforcing ideological messaging while reflecting regional diversity and social realities.
Booth-Level Tactics
Booth-Level Tactics form the operational core of the BJP’s ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army, where national digital strategy meets ground execution. Each booth unit, covering roughly 1,000 voters, is managed by trained volunteers who handle local WhatsApp groups, distribute verified digital content, and collect real-time voter feedback.
These teams personalize messages based on local demographics, caste, religion, and community priorities. Through constant data exchange with district and state IT cells, booth-level operations ensure accurate targeting, rapid mobilization, and consistent message delivery, transforming every booth into an active node of digital and electoral coordination.
Daily Content Distribution
Daily Content Distribution ensures a continuous flow of communication within the BJP’s ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army network. The National IT Cell in Delhi prepares and schedules verified multimedia content videos, infographics, quotes, and news updates, which are shared each morning with state and district IT groups.
Regional teams translate and adapt this material into local languages before forwarding it to booth-level volunteers. These volunteers then distribute it through WhatsApp groups and the Modi Mitra App to reach targeted voter segments. This structured, daily routine maintains message consistency, rapid dissemination, and sustained digital engagement across every constituency.
Structured Communication Flow
Daily Content Distribution is a disciplined process through which the BJP’s ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army maintains consistent digital engagement across its national network. The system runs on a centralized-to-local communication model in which the National IT Cell in Delhi creates and circulates official content to state- and district-level coordinators each morning.
These materials include verified videos, infographics, articles, and social media posts that align with the day’s campaign priorities or government announcements. Once received, regional teams adapt the content to local languages, add regional context if needed, and forward it to booth-level volunteers for dissemination.
Frequency and Content Volume
Each volunteer is instructed to post five to ten pieces of content daily, ensuring a steady flow of information throughout the day. The mix typically includes short videos, quotes from party leaders, infographics highlighting achievements, news headlines, and responses to trending issues.
The objective is to maintain visibility across social media platforms and WhatsApp groups without overwhelming audiences. Content scheduling follows a planned rhythm of morning motivation posts, midday updates, and evening recaps to sustain engagement over time and reinforce the message.
Verification and Messaging Discipline
Before distribution, all content passes through a verification and approval layer managed by the Delhi HQ media monitoring team. This ensures factual accuracy, consistency in tone, and alignment with the official party narrative.
Volunteers are trained to avoid unverified material and to use only authorized messages circulated through the Modi Mitra App or WhatsApp leadership groups. This control mechanism prevents misinformation and maintains a uniform communication standard across millions of digital participants.
Localization and Adaptation
Regional and district teams localize central content by translating text, adjusting examples, and incorporating local events or figures. For example, a national development message may reference a state-level project or a local leader’s contribution to increase relevance.
These localized posts help voters relate national policies to their own community experiences. The combination of central messaging and regional adaptation keeps the communication authentic and culturally resonant.
Data Tracking and Feedback Loop
The distribution process is closely monitored through analytics dashboards linked to the Modi Mitra App. Regional administrators track volunteer participation, engagement rates, and message reach daily. Volunteers submit short feedback reports on voter reactions or local discussions triggered by their posts.
This feedback travels back up the hierarchy to the district and state IT teams, which review trends and share insights with the National IT Cell. The system functions as a continuous loop, content flows downward, and data and reactions move upward.
Strategic Purpose
Daily Content Distribution ensures that the BJP’s digital communication remains active, coordinated, and measurable. The five-to-ten posts-per-day framework keeps the party’s messaging visible across social media and community networks while allowing for local adaptation.
This structure enables the Modi Mitra Digital Army to respond quickly to political developments, control narratives in real time, and maintain a consistent presence in both digital and grassroots conversations. Through disciplined scheduling and centralized oversight, the BJP holds a steady, controlled digital pulse across the nation.
Door-to-Door + IVR Outreach
Door-to-Door and IVR Outreach extend the BJP’s ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army beyond online platforms into direct, personalized voter contact. Booth-level volunteers conduct structured door-to-door visits, share verified campaign materials, collect voter feedback, and record responses through the Modi Mitra App.
This physical engagement complements the Interactive Voice Response (IVR) system, which delivers pre-recorded messages from senior leaders to targeted voter segments. The IVR network enables large-scale yet personalized communication, ensuring message consistency while reaching voters who are less digitally active. Together, these methods combine human interaction with technology-driven precision to strengthen last-mile political outreach.
Integrated Ground and Digital Communication
The BJP’s ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army combines physical and digital voter engagement through a dual system of door-to-door campaigns and IVR (Interactive Voice Response) outreach. This integrated approach ensures both personal connection and efficient large-scale communication.
Booth-level teams conduct door-to-door visits guided by data from the IT Cell, using voter lists and regional sentiment insights to target specific households. Each volunteer carries pre-approved digital material, such as videos and infographics, accessible through the Modi Mitra App. This ensures that every conversation remains consistent with the national message while addressing local issues.
Role of the Panna Pramukh
At the core of this grassroots structure is the Panna Pramukh, a volunteer responsible for approximately 60 voters (one page of the voter list, or “panna”). Each Panna Pramukh acts as the first point of contact between the party and citizens, managing both physical outreach and digital updates.
They record voter feedback, verify demographic details, and report responses through the booth-level coordination system. Panna Pramukhs use WhatsApp and the Modi Mitra App to receive daily talking points and distribute localized content, ensuring the BJP’s communication reaches every household with precision and continuity.
IVR-Based Communication System
The IVR network supports the ground campaign by automating personalized calls from senior BJP leaders to registered voters. Pre-recorded messages in regional languages highlight government achievements, upcoming events, or specific welfare schemes.
These calls strengthen the emotional link between national leadership and local voters, particularly in areas where face-to-face interaction is limited. The IT Cell tracks IVR engagement through call completion rates and response data, helping refine targeting for subsequent campaigns.
Data Collection and Feedback Loop
During door-to-door visits, volunteers collect voter data, including contact numbers, age groups, and issue preferences, enriching regional databases. This information feeds directly into the central IT system, allowing data analysts to identify trends and adjust communication priorities.
The feedback loop between ground workers, Panna Pramukhs, and regional IT coordinators ensures continuous improvement in message accuracy and voter targeting.
Coordination and Message Discipline
All outreach activities follow a structured chain of command. District coordinators supervise booth-level teams and verify that Panna Pramukhs adhere to standardized scripts and protocols. Volunteers use only verified materials shared through official digital channels to maintain message control and prevent misinformation.
The combination of door-to-door engagement, digital communication, and automated voice outreach ensures consistent, data-backed, and emotionally resonant voter contact.
Strategic Purpose
The integration of door-to-door interaction, Panna Pramukh coordination, and IVR messaging strengthens the BJP’s ability to maintain a personal yet scalable voter connection. This model merges human engagement with digital precision, allowing every household to receive tailored communication grounded in local realities and national vision.
By combining data analytics, structured volunteer management, and technological tools, the BJP’s IT Cell ensures that voter outreach remains both widespread and deeply personalized across all constituencies.
Voter Data Collection
Voter Data Collection is a central function of the BJP’s ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army, linking ground-level outreach with data-driven campaign strategy. Booth-level volunteers and Panna Pramukhs gather voter details during door-to-door visits, including contact numbers, demographics, community profiles, and issue preferences.
This information is uploaded through the Modi Mitra App and synchronized with regional and national IT databases. The data helps the party identify voter segments, track sentiment changes, and design targeted communication strategies. By combining manual collection with digital analytics, the BJP builds a continuously updated voter intelligence system that supports micro-targeted outreach across every constituency.
Structured Data-Driven Outreach
Voter Data Collection within the BJP’s ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army functions as a systematic and technology-led process designed to support micro-targeted political communication. The operation connects booth-level volunteers, regional IT teams, and the national command center through an integrated data network.
Field volunteers collect voter details during physical interactions and digital surveys, focusing on demographic attributes, occupation, community affiliations, and issue-based preferences. This data is crucial for refining campaign targeting, predicting voter behavior, and customizing regional outreach strategies.
Sakal App Integration
The Sakal App serves as the core platform for voter data entry and management. Volunteers and Panna Pramukhs use the app to record information gathered during door-to-door visits, community meetings, and local events. The app captures details such as voter names, age, gender, contact information, household size, and socio-economic indicators.
It also includes response-tracking fields to capture voter sentiment on specific government policies or political issues. All entries sync automatically with regional and national databases, creating a real-time data pipeline for campaign analysis.
Data Verification and Accuracy Checks
Each entry submitted through the Sakal App undergoes verification by regional IT supervisors to ensure accuracy and consistency. Duplicate or incomplete records are flagged automatically, while cross-checking mechanisms validate voter information against booth-level electoral rolls.
This layered review process ensures that campaign teams work with verified, actionable data. Verified data is then classified into supporter, neutral, or opposition voter categories, enabling targeted digital messaging and follow-up engagement.
Role of Ground Volunteers
Booth-level volunteers and Panna Pramukhs play a central role in maintaining the data ecosystem. They are trained to collect information systematically using standardized survey formats and update it promptly on the Sakal App.
Their local familiarity allows them to identify households, resolve address discrepancies, and record nuanced social data that digital systems alone cannot capture. Each volunteer’s performance is monitored through app-based dashboards that track daily data submissions and engagement coverage.
Data Utilization and Campaign Integration
Once compiled, voter data feeds directly into the BJP’s digital strategy network. The IT Cell uses analytics to segment audiences based on caste, religion, gender, and region. Campaign teams then tailor WhatsApp messages, IVR calls, and social media content according to these voter segments.
For example, welfare updates reach women beneficiaries, while youth-targeted content focuses on education and employment. The feedback collected through the Sakal App helps refine these strategies continuously, ensuring the message remains relevant and data-backed.
Strategic Importance
The integration of the Sakal App into voter data collection has transformed how the BJP’s IT Cell manages field intelligence. It replaces manual record-keeping with a centralized, traceable, and analytics-ready system. This allows rapid identification of swing voters, assessment of public mood, and targeted booth-level mobilization.
The structured use of technology and human coordination ensures that every data point directly contributes to electoral planning, making voter information the foundation of the BJP’s digital and grassroots campaign architecture.
Soft Interviews
Soft Interviews are an essential component of the BJP’s ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army outreach framework, designed to gather qualitative voter insights beyond numerical data. Booth-level volunteers and Panna Pramukhs conduct informal, conversational interviews with citizens during home visits, community events, or phone interactions.
These interviews focus on understanding voter perceptions, local concerns, and emotional responses to government policies. The findings are entered into digital tools like the Sakal App, helping regional and national IT teams identify sentiment patterns and refine message framing. By combining empathy-driven dialogue with data analysis, soft interviews strengthen the BJP’s ability to craft communication that feels personal, credible, and locally relevant.
Purpose and Framework
Soft Interviews are a structured yet conversational outreach method within the BJP’s ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army, designed to collect qualitative insights from voters through personal dialogue. Unlike formal surveys or data forms, these interviews emphasize tone, empathy, and natural communication.
Volunteers and booth-level coordinators conduct them during home visits, small group meetings, or follow-up calls. The goal is to identify voter expectations, concerns, and emotional responses to specific issues, helping the IT Cell refine campaign strategies and adjust communication themes.
Role of Minister Questions
The process includes a targeted questionnaire, the Minister’s Questions, and a curated list developed by senior leaders and policy strategists. These questions focus on voters’ awareness and opinions about key government programs, local governance, and ministerial performance. Examples include:
-
“Are you aware of the welfare schemes implemented in your area?”
-
“Which government program has made the most difference in your community?”
-
“What local challenges still need attention?”
Volunteers record the responses directly through digital tools such as the Sakal App or the Modi Mitra App. This data helps the IT Cell assess how effectively ministerial work translates into public sentiment and whether there are communication gaps between governance and citizens.
Data Capture and Feedback Flow
Each interviewer logs responses in real time and categorizes them by sentiment: positive, neutral, or negative. The data flows upward through regional IT teams to the national analytics unit, where patterns are analyzed to shape messaging priorities. Ministers receive briefed summaries that highlight regional feedback, recurring issues, and potential areas of improvement.
This feedback loop transforms qualitative opinions into actionable insights for both governance and communication planning.
Volunteer Training and Message Discipline
Volunteers conducting soft interviews undergo specific training to ensure neutrality, empathy, and clarity. They are instructed to listen attentively, avoid political confrontation, and document responses accurately. All interviews use verified talking points and minister-specific question templates provided by the central IT Cell.
This discipline ensures consistency across thousands of interactions, preserving message integrity while maintaining a genuine conversational tone.
Integration with Broader Campaign Strategy
The insights from these interviews inform the BJP’s micro-targeting model. Data on voter sentiment helps identify which messages resonate within specific demographics or regions. For instance, if feedback indicates low awareness of a welfare program, the IT Cell tailors local digital campaigns to emphasize that initiative.
Similarly, if dissatisfaction arises over a regional issue, volunteers escalate it for direct ministerial follow-up or to redirect the content.
Strategic Outcome
Soft Interviews, combined with Minister Questions, serve as both a listening tool and a trust-building exercise. They help humanize political communication, moving beyond one-way messaging to meaningful dialogue.
By integrating qualitative voter perspectives into the digital command structure, the BJP ensures its outreach remains grounded in public reality while maintaining data-backed precision. This system bridges governance performance, voter sentiment, and communication strategy within a unified, responsive feedback framework.
Paid & Unpaid Collabs
Paid and Unpaid Collaborations are an integral part of the BJP’s ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army communication ecosystem, designed to expand reach across digital and influencer networks. The IT Cell partners with social media creators, regional influencers, journalists, and content pages to amplify verified narratives, campaign messages, and government achievements.
Paid collaborations involve contracted influencers who produce coordinated content aligned with official talking points. In contrast, unpaid collaborations rely on volunteer creators and ideological supporters who share or adapt existing material organically.
This blended model ensures both wide-scale visibility and authentic community engagement, allowing the party’s digital communication to spread through diverse voices while maintaining narrative consistency and message discipline.
Purpose and Structure
Paid and Unpaid Collaborations form a key component of the BJP’s ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army, allowing the IT Cell to expand its digital influence through a mix of professional content creators and volunteer supporters. This system is built on a dual framework: paid collaborations that follow structured contracts and unpaid collaborations driven by ideological participation.
The objective is to scale message reach, sustain daily engagement, and maintain a steady presence across social platforms such as X, Instagram, YouTube, and regional content networks.
Paid Collaborations and Compensation Model
The paid collaboration network consists of verified digital creators, regional influencers, and media page administrators who share or produce content aligned with the party’s communication goals. These collaborators are compensated on a per-post basis, generally between ₹45 and ₹50 per post, depending on engagement metrics and content quality.
Payments are tracked digitally, and performance reports determine future assignments. The IT Cell uses this model to secure high-frequency posting during campaign periods and major political announcements, ensuring message consistency and rapid dissemination across diverse audiences.
Unpaid Collaborations and Volunteer Participation
Unpaid collaborations rely on volunteers, supporters, and organic influencers who share party content without financial incentives. Many are part of regional WhatsApp or Telegram groups managed by the Modi Mitra network. They receive verified media materials, pre-written captions, and hashtags each morning through digital briefings.
The volunteers’ participation reflects loyalty to the party’s ideology and their role in expanding authentic, community-based engagement. This unpaid segment plays an equally strategic role by making the campaign appear grassroots and citizen-driven.
Coordination and Oversight
The IT Cell’s social media coordination team oversees both paid and unpaid collaborations through regional monitoring dashboards. These systems track post frequency, audience engagement, and sentiment analysis.
Regional communication heads maintain daily logs to ensure that content adheres to the approved message framework and that paid collaborations deliver measurable results. Feedback from both networks flows upward to the national digital command, which uses the data to refine outreach tactics and audience segmentation.
Quality Control and Verification
All collaborators receive verified media kits sourced from the Delhi HQ content team. These kits include short videos, infographics, and talking points tied to ongoing campaigns, speeches, or welfare schemes. Paid influencers must submit proof of posting for verification, while unpaid collaborators are encouraged to share screenshots or engagement data voluntarily.
This system maintains message accuracy, prevents misinformation, and ensures each post contributes to measurable digital impact.
Strategic Impact
The combination of paid posts at ₹45–₹50 each and large-scale unpaid amplification creates a hybrid communication structure that blends professionalism with community participation. This model guarantees both scale and authenticity: paid influencers provide reach and visibility, while unpaid collaborators deliver credibility and organic traction.
By managing both networks through a unified IT framework, the BJP sustains continuous digital momentum, ensuring every campaign achieves maximum visibility and alignment with the broader ‘Modi Mitra’ outreach strategy.
VT/Insta Creators
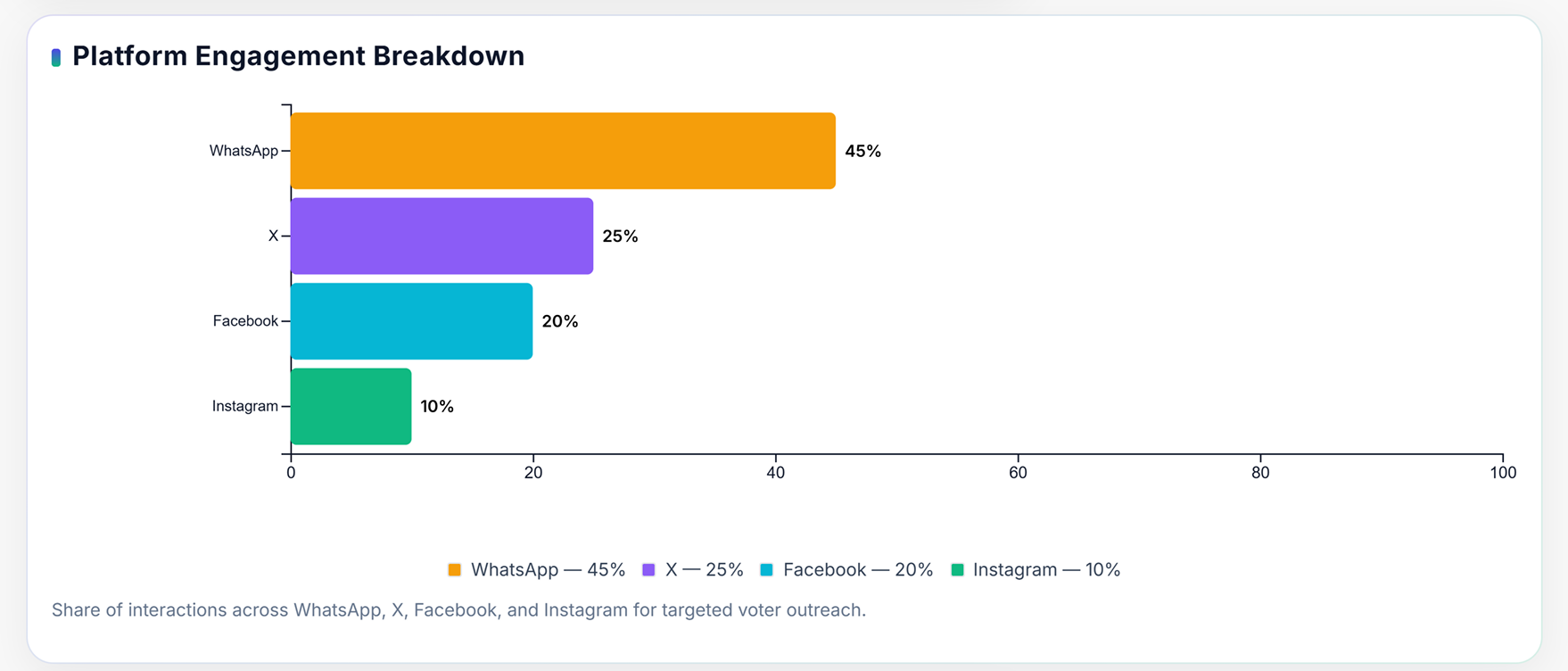
VT/Insta Creators are a specialized segment of the BJP’s ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army focused on producing short-form, high-engagement content for platforms like Instagram Reels, YouTube Shorts, and ShareChat. These creators, often part of both paid and volunteer networks, craft visually appealing videos, trend-based reels, and issue-driven clips aligned with the IT Cell’s daily communication themes.
Their content highlights leadership messages, government initiatives, and local success stories in relatable formats. The IT Cell provides them with verified media kits, captions, and talking points to ensure message consistency. By combining trend awareness with ideological storytelling, VT/Insta Creators help the party reach younger, mobile-first audiences and sustain continuous digital visibility across social media ecosystems.
VT/Insta Creators represent a focused digital unit within the BJP’s ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army, dedicated to content creation for high-engagement visual platforms such as Instagram Reels, YouTube Shorts, and ShareChat Videos. This network integrates entertainment-driven formats with political communication to reach younger, mobile-first audiences.
The creators blend trend-based storytelling, localized narratives, and visual design to present the party’s campaigns, welfare achievements, and leadership communication in concise, shareable formats.
Creator Network and Scale
Each national communication cycle targets 100 influencers per campaign, drawn from both paid and voluntary pools. These creators are selected based on their follower base, audience engagement, and platform expertise.
The IT Cell maintains a rotating roster of verified accounts that can be mobilized rapidly for coordinated content drops tied to speeches, events, or policy launches. This structured distribution ensures that political messaging reaches millions within minutes through algorithm-optimized platforms like Instagram and YouTube.
Coordination and Workflow
The digital command in Delhi provides creators with a centralized media kit that includes short videos, hashtags, captions, and guidelines for tone and visuals. Regional digital teams adapt this content into local languages and send it to their influencer clusters. Each influencer is assigned daily or weekly deliverables, typically short-form videos ranging from 15 to 60 seconds.
The content is reviewed before posting to maintain message accuracy and consistency.
Paid and Volunteer Participation
The network operates on a hybrid model. Paid influencers receive compensation for each verified post, generally ranging between ₹45–₹50, while unpaid creators contribute voluntarily as ideological supporters. Paid creators are monitored through platform analytics to track impressions, reach, and engagement rate.
Unpaid contributors often act as amplifiers, resharing paid creator content and adapting it for their local audiences. This layered structure maximizes both reach and authenticity.
Content Strategy and Messaging Goals
Each campaign theme focuses on visual storytelling that reinforces specific communication goals. For example:
-
Highlighting a welfare scheme using before-and-after visuals.
-
Showcasing local beneficiaries or community events.
-
Editing trending audio tracks with Modi speeches or slogans.
The approach combines entertainment and persuasion, ensuring political messages fit naturally into users’ social media feeds without appearing overtly propagandistic.
Oversight and Quality Control
The IT Cell’s content moderation unit reviews influencer output through a tracking dashboard. It measures post frequency, audience sentiment, and trend performance across regions. Underperforming content is revised or replaced within hours to maintain momentum.
Regular feedback loops between creators and regional IT heads ensure campaign agility and message alignment.
Strategic Outcome
By assigning 100 influencers per national target, the BJP creates a scalable, responsive, and data-driven digital ecosystem. These VT/Insta Creators act as decentralized communicators amplifying verified content, shaping perception, and countering narratives in real time.
The integration of short-form storytelling with organized influencer management has made this model one of the most efficient outreach arms of the ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army, driving consistent engagement across India’s expanding social media audience.
Real-time Trend Hijacking & Hashtag Campaigns
Real-time Trend Hijacking and Hashtag Campaigns form a rapid-response strategy within the BJP’s ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army, designed to dominate online conversations and steer public sentiment during unfolding events.
The IT Cell’s digital monitoring team tracks trending topics across platforms like X, Instagram, and YouTube, identifying opportunities to insert party-aligned narratives within minutes. Regional content units receive pre-approved media kits, images, short videos, and slogans optimized for trending hashtags.
Simultaneously, volunteer groups and paid creators amplify these posts using synchronized timing and region-specific language variations.
This coordinated approach transforms organic trends into political messaging opportunities, ensuring the party’s visibility stays at the forefront of social media discourse while maintaining message uniformity and audience relevance.
Purpose and Strategy
Real-time Trend Hijacking and Hashtag Campaigns form a rapid-response communication mechanism within the BJP’s ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army. This strategy ensures the party remains visible and influential during online discussions that gain sudden public attention.
The IT Cell’s monitoring teams use social media analytics tools to identify emerging topics on X, Instagram, YouTube, and regional platforms within minutes of their rise. Once a relevant trend is spotted, the central digital command decides whether to amplify, counter, or redirect the conversation toward a party-aligned message.
Centralized Coordination and Workflow
The Delhi-based command center leads the coordination effort. It creates verified content packs that include short videos, infographics, slogans, and templated hashtags. These assets are distributed instantly through WhatsApp, Telegram, and the Modi Mitra App to state and booth-level digital volunteers.
Within an hour of a trend emerging, regional units begin posting synchronized content, ensuring a flood of party-aligned posts appear across platforms. This timing allows the BJP’s digital presence to dominate algorithmic visibility and influence how the public perceives the event or issue.
Role of Regional and Volunteer Networks
Regional digital teams localize national hashtags and adapt captions into regional languages to achieve stronger resonance. Volunteer networks, including booth-level members and local influencers, are mobilized to post simultaneously. Each participant receives a fixed set of 5–10 approved posts with clear instructions on timing and engagement strategy.
These posts often include talking points that highlight government performance, counter opposition narratives, or align with trending topics to positive governance themes. The synchronized participation of thousands of accounts creates high engagement density, pushing BJP-related hashtags to the top of national and regional trends.
Content Creation and Trend Adaptation
Trend hijacking relies on agility. Creators within the network quickly adapt popular memes, short video formats, or viral phrases into campaign-relevant content. For instance, if a national issue trends unexpectedly, the IT Cell recontextualizes it through visuals or slogans that connect it to party initiatives or leadership messaging.
The digital teams avoid overt partisanship in early posts to ensure organic traction before gradually integrating political angles. This method provides higher algorithmic reach and engagement from neutral audiences.
Paid Collaborations and Performance Tracking
Paid influencers play an active role in early amplification. They receive pre-approved media kits and are compensated per post, typically at rates ranging from ₹4 to ₹50. Their posts help establish initial visibility, while unpaid volunteers sustain engagement over time.
Each trend campaign is tracked through engagement dashboards that measure reach, impressions, sentiment, and hashtag ranking. Underperforming campaigns are re-evaluated, with alternative hashtags or visuals deployed within hours.
Data Analysis and Feedback Loop
The IT Cell’s analytics division reviews the performance of every trend campaign using platform-level metrics. Data from these analyses is used to refine timing, tone, and content types for future campaigns. Successful hashtags are recycled across states, while less effective ones are retired. Feedback from regional heads and volunteer reports ensures that each campaign reflects genuine voter sentiment rather than only digital momentum.
Strategic Outcome
The BJP’s integration of real-time trend hijacking into its digital framework ensures message dominance during critical online conversations. This model combines speed, scale, and narrative control, allowing the party to react to breaking events within minutes and shape public discourse before opponents can respond.
The continuous coordination between paid influencers, regional volunteers, and the central IT command converts social media trends into political communication tools that sustain visibility, control narratives, and reinforce ideological consistency across India’s digital ecosystem.
Modi Mitra Digital Army – BJP’s IT Cell Network
The Modi Mitra Digital Army functions as an extensive, multi-layered communication network managed by the BJP’s IT Cell to coordinate digital outreach, data collection, and real-time voter engagement across India.
Operating through a structured hierarchy from the national headquarters in Delhi down to booth-level volunteers, the network integrates technology, analytics, and grassroots mobilization. Its ecosystem includes over 2.5 million volunteers, 5 million WhatsApp groups, and the Modi Mitra App, which links field data to central command systems.
The digital army executes micro-targeted campaigns using localized content, real-time trend hijacking, and influencer collaborations. Regional IT units translate national narratives into state-specific messaging, while booth-level coordinators distribute daily posts, collect voter sentiment, and conduct soft interviews through apps like Sakal.
Paid and volunteer influencers, including VT/Insta Creators, amplify messages through short-form videos and trending hashtags. This tightly coordinated effort among digital operations, data analytics, and on-the-ground outreach enables the BJP to maintain narrative dominance, gauge voter response, and ensure consistent messaging across every layer of its communication network.

Structure and Purpose
The Modi Mitra Digital Army functions as a coordinated digital and ground-based communication network managed by the BJP’s IT Cell. Its purpose is to maintain continuous voter engagement, control narratives, and ensure message consistency across India’s digital platforms.
The network operates through a structured hierarchy from the National IT Cell headquarters in Delhi to regional, district, and booth-level volunteers. Each level connects through digital infrastructure, including the Modi Mitra App, which links grassroots data collection with central analytics. The system allows the party to communicate directly with millions of supporters, track responses, and refine campaign strategies in real time.
National Command and Coordination
The National IT Cell in Delhi serves as the central command hub, overseeing over 150,000 regional programs, managing 2.5 million volunteers, and supervising more than 5 million WhatsApp groups. Through this infrastructure, the national team coordinates daily digital briefings, content dissemination, and data monitoring.
The command center uses real-time dashboards to track engagement, campaign sentiment, and trend activity. Each region receives content schedules, talking points, and approved visuals that align with the national narrative while allowing localized adaptation.
Regional Deployment and Micro-Targeting
Regional IT teams are responsible for adapting national communication into regional languages, local dialects, and cultural references. Each constituency has specific outreach goals, including a target of 2.5 million contacts.
Volunteers register through missed calls or app-based onboarding to join WhatsApp clusters and voter databases. This ensures that every booth has a functional digital communication chain connecting volunteers, voters, and party leadership. Regional teams also manage data enrichment, continuously updating voter details and sentiment reports from field interactions.
Digital Content Operations
The IT Cell runs a daily content cycle involving 5–10 verified posts shared across multiple platforms. Content includes graphics, short videos, and quotes that promote government initiatives, counter misinformation, or highlight regional achievements.
The Delhi HQ pre-plans around 80 percent of all material, while 20 percent is reactive content designed for real-time events. Regional content coordinators localize visuals and subtitles for social relevance. The network ensures that the same narrative reaches urban and rural audiences simultaneously through WhatsApp, Telegram, and social media amplification.
Data Integration and Apps
Voter data collection operates through digital tools such as the Sakal App and Modi Mitra App, which record household details, voter preferences, and feedback during door-to-door campaigns. Each entry is tagged with booth-level identifiers for easy analysis.
The data supports predictive modeling, helping the IT Cell design targeted messages based on caste, religion, occupation, or regional trends. Booth-level volunteers continuously update voter lists, ensuring real-time accuracy and actionable insights for campaign strategists.
Content Distribution and Influence Ecosystem
To amplify digital narratives, the BJP’s IT Cell collaborates with both paid and volunteer influencers under the Paid & Unpaid Collabs model. Paid creators receive compensation ranging from ₹45 to ₹50 per post, while volunteers participate ideologically without payment.
The influencer ecosystem includes VT/Insta Creators, short-form content producers who create videos and reels using trending formats and localized messaging. Each national campaign engages around 100 influencers to produce synchronized visual content optimized for Instagram, YouTube Shorts, and ShareChat.
Real-Time Campaign Execution
The Real-time Trend Hijacking and Hashtag Campaigns division monitors online trends 24/7 through social analytics tools. When a topic begins to trend, the IT Cell quickly produces visual and text-based content that aligns with the issue and links it to party narratives.
Regional units receive these materials instantly, ensuring synchronized posting across thousands of accounts. This strategy ensures visibility dominance and shapes public perception during fast-moving digital conversations.
Field-Level Operations and Voter Engagement
Ground-level communication mirrors digital engagement through door-to-door outreach and IVR-based voter calls led by Panna Pramukhs. Volunteers collect feedback, conduct soft interviews, and use Minister Questions to assess awareness of government programs.
Responses are logged digitally for sentiment analysis. Regional coordinators then use these insights to refine local campaigns and escalate feedback to ministers for policy-level communication adjustments.
Integration of Technology and Human Networks
The Modi Mitra Digital Army merges digital infrastructure with grassroots mobilization. Volunteers serve as both data collectors and content distributors, ensuring two-way information flow. Technology enables message delivery at scale, while human interaction sustains trust and credibility.
Regional IT heads oversee verification, ensuring data accuracy and message discipline.
Strategic Impact
Through this coordinated digital command, the BJP’s IT Cell achieves precise message targeting, rapid trend engagement, and sustained digital visibility across all platforms and regions. The Modi Mitra Digital Army operates as a national communication engine, linking analytics, content, and grassroots action, ensuring the party’s voice remains unified, measurable, and responsive to both online discourse and on-the-ground realities.
Digital Army Hierarchy – National to Booth-Level
The Digital Army Hierarchy within the BJP’s ‘Modi Mitra’ network functions through a structured system that links the National IT Cell headquarters in Delhi with state, district, constituency, and booth-level teams.
At the top, the national command manages coordination, strategy, and content creation for more than 150,000 regional programs, directing digital communication across all states. State and district IT cells translate these directives into regional languages and culturally relevant formats, maintaining message consistency across diverse audiences.
Constituency-level digital coordinators oversee volunteer networks and data operations, ensuring that voter outreach aligns with booth-level engagement. Each booth operates a dedicated WhatsApp group led by trained volunteers who share daily content, gather feedback, and record voter sentiment using digital tools such as the Modi Mitra App and Sakal App.
This hierarchy creates a seamless communication flow from national leadership to local communities, enabling rapid response, accurate messaging, and sustained voter engagement across both digital and grassroots levels.
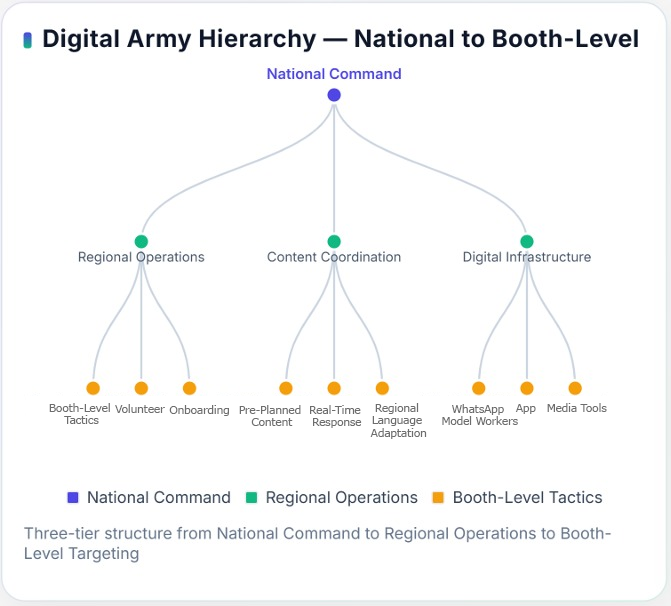
Structure and Chain of Command
The Digital Army of the BJP’s ‘Modi Mitra’ network operates through a tightly organized, multi-tier structure that connects the National IT Cell headquarters in Delhi with regional, district, constituency, and booth-level digital teams.
The hierarchy ensures that every layer of communication from content creation to voter engagement follows a centralized directive. The National IT Cell manages overall strategy, data infrastructure, and digital operations, while state and district cells handle adaptation, translation, and localized execution.
This vertical chain enables seamless coordination among digital messaging, on-the-ground outreach, and feedback loops.
National-Level Coordination
At the top, the National IT Cell serves as the command center for all digital initiatives. It supervises more than 150,000 regional programs, coordinates a network of over 2.5 million volunteers, and manages approximately 5 million WhatsApp groups.
The national team sets daily communication themes, approves creative assets, and monitors performance metrics through real-time dashboards. Directives flow downward each morning through internal communication channels such as the Modi Mitra App and encrypted WhatsApp groups.
Every message issued by the central team is tagged for tracking to prevent unauthorized or inconsistent content circulation.
State and District-Level Implementation
State and district IT Cells act as operational hubs that translate national directives into region-specific campaigns. Teams in these units manage digital language adaptation, regional influencer collaborations, and local content distribution.
They also oversee district-level WhatsApp clusters and Telegram groups that connect volunteers, local leaders, and digital creators. These regional teams report daily analytics and voter sentiment to Delhi HQ, ensuring that national campaigns reflect regional realities and that field data informs message adjustments.
Constituency-Level Coordination
Each parliamentary or assembly constituency has a designated digital coordinator responsible for executing daily instructions and ensuring booth-level performance. They monitor volunteer participation, track voter engagement, and supervise data collection through the Sakal and Modi Mitra Apps.
Constituency heads also manage real-time communication between district teams and booth volunteers, providing updates on trending issues, opposition messaging, or community-specific reactions. This layer serves as the critical bridge between regional management and grassroots execution.
Booth-Level Operations
At the foundation of the digital hierarchy, booth-level teams serve as the direct link to voters. Each booth typically maintains a dedicated WhatsApp group, managed by a trained volunteer or Panna Pramukh. Volunteers share 5–10 posts daily that include verified graphics, short videos, and text messages supplied by higher units.
They also gather feedback, conduct soft interviews, and log voter sentiment data into the Modi Mitra App. Booth teams often coordinate door-to-door outreach, IVR calls, and community meetings, ensuring online communication aligns with real-world engagement.
Data Integration and Feedback Flow
All data collected at the booth level, including engagement metrics, feedback, and demographic details, is uploaded through digital platforms and synced with regional databases. This information supports predictive modeling, sentiment mapping, and micro-targeted messaging.
The feedback flow is two-way: while the national unit provides directives and campaign material, booth-level teams supply insights that influence future content, slogans, and outreach strategies.
Oversight and Accountability
Each hierarchical layer maintains performance accountability. Regional IT heads submit progress reports to state coordinators, who compile weekly summaries for national review. Engagement statistics, message reach, and data accuracy are evaluated regularly.
Activity levels rank volunteers, and inactive clusters are reorganized to maintain consistency. This system ensures operational discipline and minimizes communication delays across India’s vast volunteer network.
Strategic Function
The Digital Army hierarchy transforms the BJP’s IT network into a coordinated communication engine that links national strategy with hyperlocal execution. Its structure allows the party to maintain real-time control over narrative framing, respond rapidly to emerging events, and monitor voter engagement from Delhi to every polling booth.
By combining data analytics, structured communication, and localized execution, the Digital Army sustains both scale and precision, making it one of the most organized digital-political networks in the country.
Volunteer Onboarding
Volunteer Onboarding within the BJP’s ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army is a structured process created to recruit, verify, and connect supporters into the party’s digital communication network. The process usually begins through missed call registrations, online forms, or local outreach campaigns run by booth-level teams.
Once registered, volunteers receive verification links through the Modi Mitra App, which connects them to official WhatsApp or Telegram groups.
New volunteers undergo digital orientation sessions that explain content distribution methods, voter engagement practices, and message coordination rules. They are provided with daily content materials, regional-language instructions, and simple performance-tracking tools. Each volunteer is assigned to a booth-level digital cluster for monitoring and coordination.
This organized onboarding model allows the party to expand participation quickly while ensuring message discipline, data accuracy, and consistent communication throughout the Modi Mitra Digital Army network.
Purpose and Design
Volunteer Onboarding within the BJP’s ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army is a structured and technology-driven process aimed at rapidly expanding the party’s digital communication base while maintaining message control and operational discipline.
It connects interested citizens, supporters, and social media users to the party’s organized digital network, enabling them to participate in campaigns, share content, and engage voters. The process ensures every new member is verified, trained, and linked to a specific operational unit within the hierarchy from national to booth level.
Registration and Verification
The onboarding process begins through multiple entry points, such as missed-call registration numbers, online sign-up forms, or direct outreach by local volunteers. Once registered, new participants receive verification links through the Modi Mitra App.
This step confirms identity, location, and constituency mapping. The app automatically assigns volunteers to district or booth-level digital groups, ensuring every new member is connected to a local communication chain. Verification protocols prevent duplicate entries and ensure all participants operate within authorized digital clusters.
Digital Orientation and Training
After verification, volunteers undergo structured digital orientation sessions. These sessions, conducted online or in small regional groups, cover communication ethics, message discipline, and voter interaction techniques. Volunteers learn how to use official communication tools, including the Modi Mitra App, WhatsApp clusters, and Telegram channels. Training modules include:
-
How to share and verify official content.
-
Voter engagement best practices during door-to-door or social media outreach.
-
Use of sentiment feedback tools to record voter opinions.
-
Digital conduct and security awareness to prevent misinformation or data leaks.
This training ensures that every volunteer understands both their responsibilities and the operational boundaries of the digital network.
Integration into the Communication System
Once trained, volunteers are added to region-specific WhatsApp or Telegram groups and receive daily content packs from district or state-level coordinators. These packs typically contain 5–10 verified posts, including graphics, short videos, and issue-based messages tailored to their region.
Volunteers are expected to post this content on their social media accounts and in community groups, as outlined in the daily schedule. Each post is monitored for reach and engagement using analytics dashboards connected to the IT Cell’s data system.
Assignment and Accountability
Every volunteer is mapped to a booth-level cluster managed by a digital coordinator or Panna Pramukh. Coordinators track participation, content activity, and feedback submissions. Volunteers who demonstrate higher engagement and accuracy are often promoted to supervisory or content distribution roles.
This accountability structure ensures consistent performance and provides clear upward mobility within the digital army. Regular feedback from regional IT heads helps refine the process and address gaps in training, communication, or participation.
Tools and Technology
The Modi Mitra App is central to the onboarding process. It functions as a hub for registration, verification, content distribution, and feedback reporting. The app also integrates with analytics tools that measure volunteer activity, voter engagement, and sentiment trends.
These insights feed directly into the national IT Cell’s central dashboard, allowing real-time adjustments to campaign strategy. App-based coordination replaces manual record-keeping and ensures transparency in volunteer management.
Continuous Engagement and Retention
To maintain motivation, volunteers receive periodic digital badges, certificates, or invitations to online meetings with party leaders. Regular communication through broadcast messages and live sessions helps sustain engagement. Volunteers are also encouraged to participate in issue-based drives, hashtag campaigns, and localized awareness events. This continuous involvement transforms passive digital supporters into active field participants who reinforce both online and offline narratives.
Strategic Function
Volunteer Onboarding ensures scalability, discipline, and message synchronization across India’s largest political communication network. By combining mobile technology, local supervision, and real-time analytics, the BJP’s IT Cell transforms ordinary citizens into structured digital operators.
This approach strengthens both the reach and credibility of the party’s communication system, ensuring that every volunteer contributes meaningfully to the data-driven, message-controlled operations of the Modi Mitra Digital Army.
Real-Time Response
Real-Time Response within the ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army focuses on ensuring immediate and coordinated reactions to news developments, opposition statements, and trending narratives. The network operates through layered WhatsApp and Telegram groups where verified volunteers receive rapid-response talking points and pre-approved media content from central or state-level IT coordinators.
Once a topic trends on social media or appears in mainstream news, the digital command team drafts short, fact-checked responses and distributes them through the Modi Mitra App. Volunteers then deploy this content across platforms such as X (Twitter), Instagram, and Facebook, ensuring message consistency and speed. Analytics dashboards monitor engagement and track which narratives gain traction.
This structure allows the BJP’s IT Cell to dominate information cycles within minutes, manage misinformation, and frame issues in the party’s favor. The real-time mechanism keeps online communication in sync with field campaigns, strengthening both perception control and the efficiency of political messaging.
Objective and Function
The Real-Time Response mechanism within the ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army serves as a rapid reaction system designed to manage, influence, and control online discourse across digital platforms. It ensures that the BJP’s IT Cell responds instantly to emerging news, opposition statements, misinformation, or viral trends.
The process allows the party to maintain narrative dominance by deploying pre-approved talking points and multimedia content through a tightly managed digital command structure.
Monitoring and Detection
The IT Cell’s monitoring teams track social media feeds, online news, and messaging apps around the clock using keyword alerts, sentiment analytics, and media scanning tools. Dedicated analysts in national and state-level digital command centers identify potential flashpoints, such as critical remarks by opposition leaders, trending hashtags, or misinformation targeting the government or the Prime Minister. Once identified, the issue is flagged to content editors and communication leads who draft a concise response strategy within minutes.
Coordination and Command Flow
Once a response is finalized, it flows through the established hierarchy. The national digital team communicates with state IT heads, who relay messages to district coordinators and booth-level volunteers.
Coordination occurs through encrypted WhatsApp and Telegram groups, segmented by geography and function. Each level is responsible for ensuring message discipline, speed, and consistency. The Modi Mitra App serves as a central hub for content delivery and tracking, pushing verified text, video, and infographics directly to volunteer dashboards.
Content Deployment
Volunteers receive ready-to-use response kits that include short text statements, pre-designed images, and hashtags optimized for trending algorithms on platforms like X (Twitter), Instagram, and Facebook.
These are deployed within a 15 to 30 minute window after issue identification, ensuring synchronized nationwide posting. Volunteers are instructed to adapt tone and language to local audiences but must not alter the central narrative. State-level content teams often localize graphics or add regional-language captions before circulation to maximize relatability and reach.
Verification and Fact Management
To maintain credibility, all content is vetted by digital fact-checking units embedded within the IT Cell. These teams cross-verify claims, sources, and statistics before dissemination. This ensures that the response remains defensible in mainstream media debates and avoids the risk of misinformation.
When misinformation against the party is detected, the Real-Time Response team immediately releases clarification material supported by evidence, official documents, or video clips. This method neutralizes false narratives while reinforcing the party’s credibility among digital audiences.
Analytics and Feedback Loop
Post-deployment, analytics systems measure content reach, engagement, and shifts in sentiment in real time. Data from social platforms, WhatsApp engagement trackers, and the Modi Mitra App feed into a centralized dashboard accessible to communication heads.
The analysis identifies which narratives perform best across states or demographics, allowing quick adjustments in tone or messaging strategy. Coordinators share daily performance summaries with state and district teams to refine ongoing campaigns.
Synchronization with Field Operations
The digital response network operates in tandem with offline campaign machinery. Booth-level teams update digital coordinators on local issues and opposition activities, enabling rapid, localized responses. Similarly, messages crafted at the national level often support real-world political events, press briefings, or rallies.
This integration between digital and ground-level action ensures message consistency and amplifies public visibility through multiple channels.
Strategic Impact
The Real-Time Response structure functions as both an information defense mechanism and an influence amplifier. By maintaining narrative control, the BJP’s IT Cell prevents negative issues from escalating and ensures its viewpoints dominate social media timelines.
The speed and scale of coordination from national offices to booth-level volunteers transform this system into a highly efficient digital war room. It reinforces the party’s ability to engage citizens continuously, correct narratives instantly, and sustain political momentum across all media formats.
Regional Language Adaptation
Regional Language Adaptation within the ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army ensures that the BJP’s digital communication reaches every linguistic and cultural audience across India. The IT Cell’s regional content teams translate, localize, and tailor national narratives to match local sentiment, idioms, and political priorities.
Each state- and district-level unit receives centrally approved material, adapted into regional languages such as Hindi, Tamil, Telugu, Bengali, Marathi, Kannada, Malayalam, and Assamese, before dissemination.
This process goes beyond translation. Regional teams modify tone, imagery, and issue framing to align with local cultural values and political contexts. For example, campaign themes about welfare or nationalism are expressed using region-specific examples and community references.
Content is distributed through localized WhatsApp and Telegram clusters, ensuring that the message resonates emotionally and linguistically with target voters.
By tailoring language and context, the BJP’s IT Cell strengthens its outreach in non-Hindi-speaking states, builds regional trust, and helps prevent communication gaps between the central leadership and local audiences. Regional Language Adaptation transforms national messaging into locally relevant political communication, making the ‘Modi Mitra’ network a multilingual digital force with deep voter penetration.
Purpose and Role
Regional Language Adaptation is a central component of the ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army’s communication framework. Its primary goal is to make political messaging accessible, relatable, and culturally relevant across India’s diverse linguistic regions.
The BJP’s IT Cell manages this through a structured localization process that ensures national narratives resonate within different state and district contexts. The method combines translation accuracy, cultural sensitivity, and audience segmentation to strengthen regional-level voter engagement.
Process and Structure
The adaptation process begins at the national command center, where the content team prepares core messages, graphics, and videos. These materials are then distributed to regional IT coordinators who oversee translation, tone adjustment, and contextual rewriting. Each state and district-level digital unit employs language specialists and local communicators to ensure the content reflects the linguistic nuances of the area.
For instance, a welfare message crafted in Hindi for North India is translated into Tamil, Telugu, or Kannada with locally relevant examples and idioms to maintain authenticity.
The Modi Mitra App serves as the primary distribution platform. Once regional communication leads approve the translated content, it is uploaded to the app and delivered directly to booth-level volunteers through WhatsApp or Telegram clusters. Volunteers then circulate it across community networks, ensuring consistent message delivery in the local language.
Cultural Customization
Regional adaptation extends beyond language. It incorporates local references, cultural imagery, and community values to enhance emotional connection. Campaigns highlighting welfare initiatives or governance achievements are framed using regional festivals, leaders, and local success stories.
This approach ensures that political messages align with state-level political dynamics, making the communication appear organic rather than centrally imposed.
Regional teams also adapt visual content, including posters and videos, to match state-specific aesthetics such as color palettes, typography, and regional symbols. This customization increases relatability and helps content blend seamlessly with local media ecosystems.
Coordination and Oversight
The IT Cell maintains strict oversight through a multi-tier review system to ensure consistency with national messaging. Each localized output passes through digital coordinators who check for factual accuracy, ideological alignment, and tone control.
Regional teams receive daily feedback from the central command, allowing quick revisions when local sentiment shifts. This coordination between central and regional layers helps the party maintain message unity while respecting linguistic diversity.
Platforms and Deployment
Regional Language Adaptation operates across multiple digital platforms. WhatsApp remains the primary tool for direct voter communication, while localized campaigns are amplified through Facebook Pages, Instagram Reels, and YouTube Shorts in regional languages.
The content timing and phrasing are optimized for local consumption habits, morning political updates, evening video clips, and weekend summaries, ensuring continuous visibility.
Impact and Effectiveness
This multilingual communication strategy has expanded the BJP’s digital reach far beyond Hindi-speaking regions. It strengthens regional political alignment by creating a sense of inclusion among non-Hindi-speaking voters. The approach also reduces dependence on local intermediaries by empowering volunteers with pre-localized content.
As a result, the Modi Mitra network achieves consistent message penetration across states, blending national-level narratives with local emotional appeal.
Strategic Outcome
Regional Language Adaptation converts a centralized digital structure into a federated communication model capable of operating in India’s linguistically diverse environment. It ensures that each message retains its ideological clarity while adapting to the unique character of every region.
This framework not only amplifies the BJP’s digital visibility but also reinforces linguistic inclusivity, enabling the ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army to function as a multilingual, culturally attuned communication network that sustains daily voter engagement nationwide.
Regional IT Cell Deployment
Regional IT Cell Deployment forms the operational backbone of the ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army, ensuring that the BJP’s centralized digital strategies are executed effectively at the state, district, and booth levels. Each regional IT Cell functions as a decentralized command unit responsible for implementing national directives, coordinating digital volunteers, and tailoring communication to match local political and cultural contexts.
These regional cells are staffed with trained digital coordinators, data analysts, and content managers who oversee messaging consistency and audience segmentation. Their work includes managing WhatsApp and Telegram networks, supervising social media accounts, and gathering feedback on voter sentiment. The deployment model ensures that every region has an agile digital infrastructure capable of real-time coordination with the national command center.
Regional IT Cells also collaborate with local influencers, booth-level workers, and media teams to enhance message reach. They handle localized content creation, including regional graphics, short videos, and voice notes that align with both linguistic and cultural preferences. This structure enables rapid response to local developments while maintaining alignment with central narratives.
By deploying IT Cells across all major regions, the BJP’s digital network achieves uniformity in communication, speed in execution, and adaptability in message framing. The system transforms the ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army into a nationwide yet locally attuned digital force capable of sustaining continuous engagement with voters at every level.
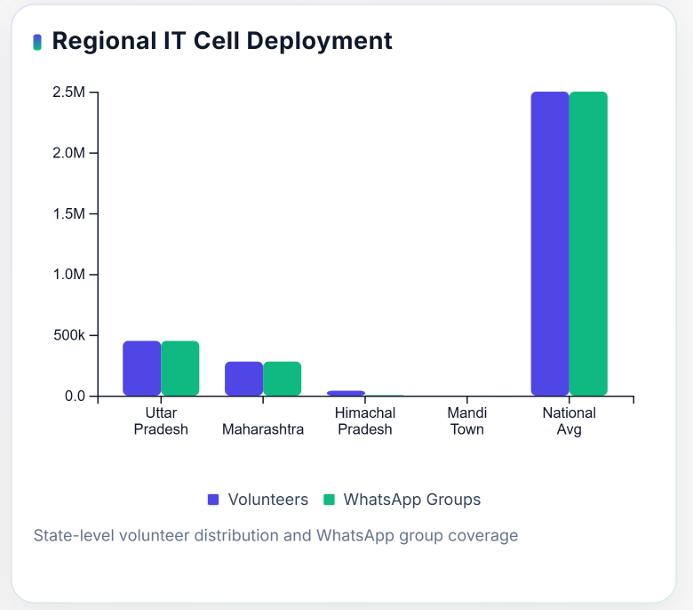
Regional IT Cell Deployment forms the operational framework that connects the BJP’s national digital command to state and district-level networks under the ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army initiative. This structure enables consistent, data-driven communication across India while maintaining the flexibility to adapt to local contexts.
The deployment relies on volunteer-based digital coordination systems supported by WhatsApp groups, which act as the core communication and mobilization channels.
Scale and Distribution
The scale of deployment varies across states, reflecting differences in population density, digital penetration, and political importance. Uttar Pradesh leads the network with approximately 450,000 digital volunteers and 430,000 WhatsApp groups. Maharashtra follows closely with around 300,000 volunteers and 290,000 active groups.
Smaller states like Himachal Pradesh maintain about 50,000 volunteers and 45,000 WhatsApp clusters. Interestingly, Mandi Town currently shows no recorded deployment activity, indicating either limited local coordination or pending rollout.
Across all states, the national average for engagement stands at around 2.5 million volunteers and an equivalent number of WhatsApp groups, marking one of the largest organized digital political infrastructures in India. This network allows regional teams to broadcast messages, collect voter feedback, and track responses in real time through hierarchical communication flows.
Function and Coordination
Each regional IT Cell operates as an extension of the central command, translating national messaging into state-specific narratives while preserving core ideological consistency. These units coordinate directly with booth-level digital volunteers who manage WhatsApp groups, share content, and monitor engagement metrics.
The use of real-time communication ensures a quick response to opposition statements, local controversies, or viral misinformation.
Regional coordinators oversee volunteer onboarding, training, and performance tracking through the Modi Mitra App. They ensure that content distribution follows daily schedules and that volunteers maintain message discipline. This coordination also involves ongoing communication between state IT heads and the national digital team to align on campaigns, hashtags, and event coverage.
Data and Communication Infrastructure
The WhatsApp-based network serves both as a broadcasting and a feedback mechanism. Each group, organized by booth or ward, disseminates official content, including videos, infographics, and talking points, often in sync with national announcements. The volunteer count per group is monitored through internal dashboards to identify high-engagement regions and underperforming zones.
The high density of volunteers in Uttar Pradesh and Maharashtra highlights the BJP’s focus on electorally strategic states. At the same time, smaller networks in hilly or urban regions, such as Himachal Pradesh and Mandi, indicate targeted outreach adjustments based on geography and connectivity.
Strategic Implications
The regional IT deployment model enables precise micro-targeting, ensuring that content reaches every demographic segment through localized digital ecosystems. By combining centralized control with regional adaptability, the BJP maintains a rapid-response structure capable of influencing narratives within minutes of an event or controversy.
This approach transforms the ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army from a top-down communication network into a decentralized, action-oriented digital movement. It allows the party to maintain message consistency at scale while empowering regional teams to operate with autonomy suited to their political terrain.
Network Operations & Content Distribution
Network Operations and Content Distribution form the functional core of the ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army, ensuring a seamless flow of information from the national IT Cell to booth-level volunteers across India. The system operates on a structured hierarchy where the central command generates daily talking points, campaign materials, and multimedia content, which are then disseminated through state, district, and booth-level digital coordinators.
The process relies heavily on WhatsApp and Telegram networks, each managed by dedicated volunteers who handle group creation, member verification, and post scheduling. Every volunteer typically circulates five to ten pieces of content per day, including videos, graphics, and voice messages aligned with the party’s communication strategy. Regional IT Cells translate and localize these materials to align with linguistic and cultural contexts, ensuring consistent message delivery while maintaining local resonance.
Content distribution also incorporates real-time feedback loops. Regional coordinators monitor engagement levels, track message reach, and report analytics to the central command for daily optimization. This data-driven structure allows the network to identify active regions, assess message effectiveness, and refine upcoming campaigns.
Through this coordinated, scalable model, the BJP’s IT Cell maintains a continuous digital presence, ensuring that every volunteer, group, and region contributes to a unified, responsive national communication system.
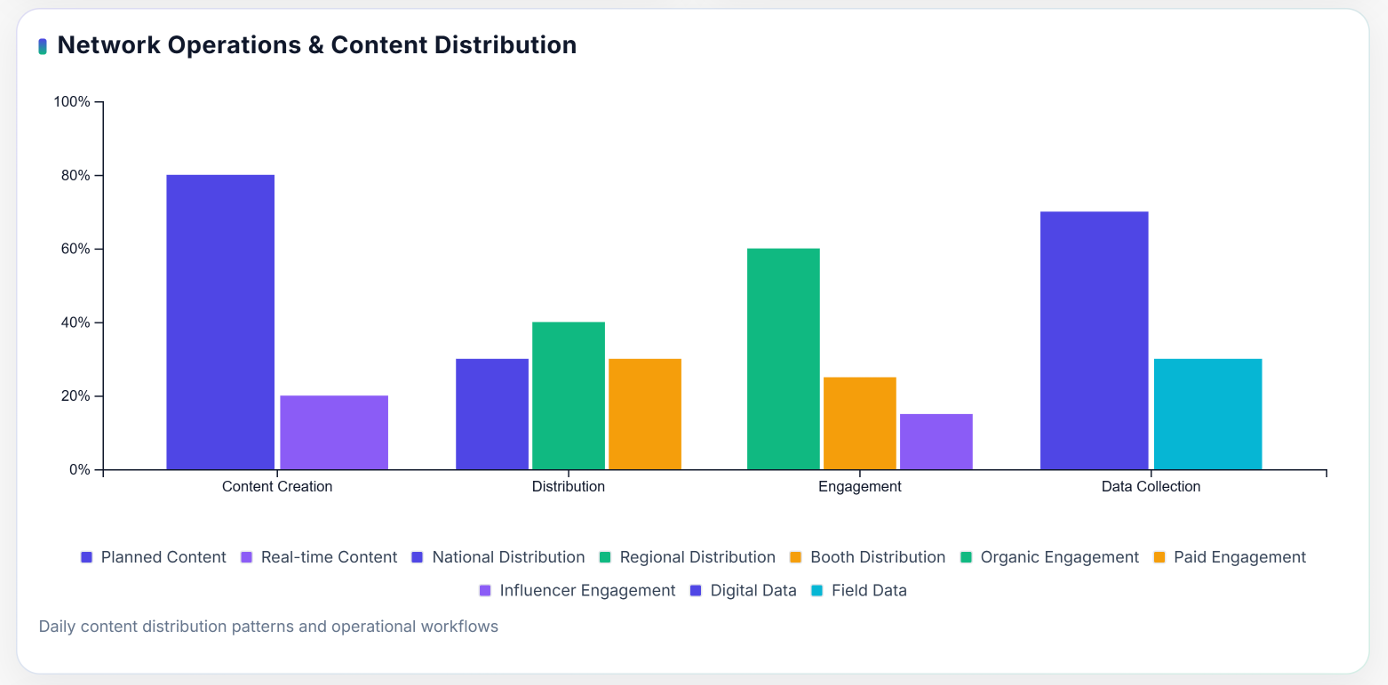
The ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army’s Network Operations and Content Distribution framework operates as a data-driven communication ecosystem designed to synchronize national narratives with regional outreach. It combines centralized strategy, structured distribution, and field-based engagement to maintain consistent messaging and maximize audience reach across multiple digital layers. The model reflects an advanced balance between planned coordination and real-time adaptability, ensuring message precision and responsiveness to public sentiment.
Content Creation Structure
Content production within the Digital Army follows an 80–20 ratio between planned and real-time materials. Approximately 80 percent of content is pre-scheduled, curated by the national command center, and distributed to regional and booth-level volunteers through structured communication channels. These materials include campaign visuals, infographics, short videos, and ideological narratives aligned with ongoing political priorities.
The remaining 20 percent of content is reactive, produced in response to breaking developments, trending topics, or opposition activity. This ensures the network remains relevant in public discourse while maintaining message consistency.
Distribution Framework
Content distribution is structured across three operational levels: national, regional, and booth. Around 30 percent of content originates at the national level, focusing on high-impact political messaging, leader communication, and nationwide campaigns.
Another 40 percent is adapted and disseminated through regional IT Cells, which localize materials by language and cultural context. The final 30 percent is distributed at the booth level by grassroots digital volunteers who personalize outreach for local communities. This hierarchical model ensures comprehensive message penetration from the national narrative to the individual voter.
Engagement Strategy
Engagement across platforms is segmented into three primary categories. Organic engagement contributes roughly 60 percent, driven by volunteer-led sharing, discussions, and community participation. Paid engagement accounts for 25 percent, covering sponsored posts, boosted videos, and targeted audience outreach on social platforms.
Influencer engagement accounts for the remaining 15 percent, coordinated through strategic collaborations with micro and regional content creators who amplify the BJP’s messaging through authentic, relatable voices.
Data Collection and Intelligence
Data collection supports both strategy formulation and real-time adjustments. Approximately 70 percent of insights come from digital channels such as social media analytics, app usage patterns, and WhatsApp group metrics.
The remaining 30 percent comes from field data gathered by booth-level volunteers through feedback mechanisms and direct voter interaction. This dual-source intelligence allows the command center to refine narratives, adjust regional strategies, and measure message effectiveness through measurable engagement trends.
Operational Efficiency
The integration of digital communication, regional adaptation, and feedback analytics makes the ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army one of the most structured political IT ecosystems in India. Its operation ensures message discipline, localized resonance, and rapid adaptability to shifting political or media conditions.
By combining national-scale coordination with hyperlocal execution, the network achieves both control and agility, enabling continuous alignment between the central digital strategy and ground-level political communication.
Strategic Campaign Framework
The Strategic Campaign Framework of the ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army defines how the BJP’s IT Cell plans, executes, and measures digital political communication across India. It integrates national messaging with localized outreach to ensure consistency, precision, and adaptability in voter engagement.
Campaigns are structured around pre-planned narratives, real-time responses, and data-driven targeting.
At the national level, campaign objectives and talking points are designed by the central IT Cell, aligning with key political events, government announcements, or opposition narratives. These messages are distributed through regional IT units, which translate and adapt them into local languages and contexts before reaching booth-level volunteers.
Each volunteer acts as a micro-communicator, amplifying content within their social circles through WhatsApp, Facebook, and Instagram.
The framework also incorporates feedback and analytics loops, allowing campaign coordinators to track message reach, engagement, and sentiment shifts. This real-time intelligence helps refine upcoming communication cycles, ensuring that digital outreach stays relevant and responsive.
By combining centralized strategy with decentralized execution, the framework turns the ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army into a synchronized, continuously active campaign network capable of shaping public perception across multiple layers of Indian society.
National Command and Coordination
The ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army operates under the supervision of the BJP IT Cell National Headquarters, which manages over 150,000 digital workers through the Modi Mitra App Network. This centralized command defines the communication tone, message themes, and content calendar for all regions.
It also oversees digital volunteer registration, performance tracking, and daily dissemination of campaign materials. Each volunteer receives curated content packets that align with the party’s messaging priorities, ensuring nationwide consistency and control over narrative flow.
Regional Operations and Onboarding
At the regional level, the system targets approximately 2.5 million digital interactions per constituency. Volunteers are onboarded instantly via missed-call registration campaigns, which link them to the Modi Mitra App for verification and role assignment. Regional operations focus on digital training, data collection, and micro-coordination with district IT teams.
This structure enables real-time mobilization during campaigns and allows regional managers to adapt content to linguistic and social nuances while maintaining alignment with the central directive.
Content Coordination and Localization
Roughly 80 percent of all content is pre-planned and produced at the Delhi headquarters, covering themes such as government achievements, opposition responses, and upcoming political events. These materials include text posts, videos, infographics, and voice clips.
Regional content teams handle translation, dubbing, and adaptation into local languages to match regional tone and voter demographics. The remaining 20 percent of content focuses on rapid-response campaigns, driven by trending topics, breaking news, or opposition statements. Local video production units support quick turnaround of this real-time material to maintain relevance across digital channels.
Booth-Level Tactics and Ground Activation
Booth-level operations form the grassroots foundation of the campaign. Over 5,000 entry points are maintained through the party’s micro-volunteer system. Each booth employs a Panna Pramukh, a digital ground coordinator responsible for household-level outreach. They conduct door-to-door visits, distribute digital materials, and engage voters through Interactive Voice Response (IVR) campaigns.
This hybrid model of physical and digital mobilization reinforces national narratives through personal voter contact. The booth-level approach also serves as a feedback channel, capturing on-ground sentiment for the regional command to analyze.
Micro-Targeting and Data Intelligence
Micro-targeting is central to the Digital Army’s campaign framework. Voter outreach is segmented by caste, religion, region, and economic group to refine message delivery. Each segment receives localized content designed to address cultural values and socio-political preferences.
Data analytics derived from the Modi Mitra App, WhatsApp engagement, and field reports guide content customization and timing. In states such as Uttar Pradesh and Maharashtra, this segmentation enables hyper-personalized digital outreach, linking digital propaganda directly to booth-level voter engagement.
Operational Integration
The Strategic Campaign Framework integrates national command with regional adaptability and booth-level precision. It ensures that every volunteer, coordinator, and regional unit operates within a synchronized information network. Centralized message creation, regional translation, and hyperlocal distribution together form a continuous communication loop.
Through this model, the BJP’s IT Cell maintains message uniformity, real-time responsiveness, and measurable digital influence, making the Modi Mitra network a scalable and disciplined campaign infrastructure that connects digital strategy to voter sentiment on the ground.
State-Level Implementation – Key Examples
The state-level implementation of the ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army demonstrates how the BJP’s IT Cell adapts its centralized digital strategy to diverse regional contexts. Each state functions as an operational hub with localized structures, language adaptation, and demographic-specific outreach.
While the national command sets the communication agenda, state IT Cells handle translation, coordination with district leaders, and on-ground data collection to ensure that digital engagement aligns with regional sentiment and electoral priorities.
In Uttar Pradesh, approximately 450,000 volunteers and 430,000 WhatsApp groups form the backbone of the state’s digital ecosystem. This extensive network supports caste and religion-based targeting, especially among OBC and Dalit communities. Maharashtra follows a similar pattern with 300,000 active volunteers and 290,000 WhatsApp groups, focusing on urban digital outreach and localized influencer engagement.
Himachal Pradesh, though smaller in scale, maintains nearly 50,000 volunteers and 45,000 WhatsApp groups, ensuring coverage across all assembly segments. Even smaller towns like Mandi have adopted structured communication setups through micro-volunteer networks linked directly to district IT coordinators.
This tiered implementation ensures message discipline while accommodating linguistic and cultural variations across states. By combining centralized message design with regional flexibility, the Digital Army sustains high engagement rates and consistency in political communication, effectively translating national digital strategy into local voter mobilization.
Himachal Pradesh
The ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army in Himachal Pradesh operates through an extensive grassroots network of 8,000 WhatsApp groups, ensuring one group per booth for complete coverage across the state. This structure allows each booth-level unit to manage digital communication and voter outreach independently while maintaining coordination with district IT Cells.
Regional coordinators monitor message consistency and engagement, ensuring that every local narrative aligns with the BJP’s central communication plan. The one-group-per-booth strategy maximizes precision in information flow and ensures that political messaging reaches every cluster of voters, even in remote areas.
Mandi Town
In Mandi, a focused hyperlocal digital model has been established with around 400 WhatsApp groups managed by 500 active volunteers. Each volunteer is responsible for group moderation, content circulation, and real-time voter interaction.
The system emphasizes two-way communication, gathering feedback from the ground and relaying it to district teams for content adjustment. This micro-scale deployment model allows Mandi to function as a pilot zone for digital testing, assessing message resonance, and refining communication tactics before statewide rollouts.
Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh represents one of the most data-driven digital ecosystems within the BJP’s structure, with 163,000 members operating under each regional IT Cell. This network specializes in cas-te and religion-based microtargeting, tailoring messages to specific voter segments.
Dedicated content modules address caste dynamics, regional concerns, and community narratives, helping the party build ideological alignment across varied demographics. The sheer size of the volunteer base allows rapid mobilization during election cycles, ensuring saturation-level message penetration across both rural and urban constituencies.
Maharashtra
In Maharashtra, the digital outreach is urban-centric, reflecting the state’s concentration of digital users in major cities. The booth-level network is designed to integrate influencer partnerships and micro-volunteer outreach. Local digital creators and youth influencers promote region-specific messages through short videos, memes, and vernacular posts.
These efforts are coordinated with city-level IT Cells to sustain daily engagement across platforms such as Instagram and X (formerly Twitter). The Maharashtra model highlights how the Modi Mitra network adapts its campaign style to urban digital behavior, blending booth-level structure with influencer-driven amplification.
Content Distribution & Engagement Tactics
The ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army operates a structured and data-driven content distribution model designed to synchronize national messaging with regional and booth-level execution.
Approximately 80 percent of the content is pre-planned by the BJP IT Cell’s central headquarters in Delhi, covering key narratives such as government achievements, social welfare programs, and counter-campaigns against opposition messaging. The remaining 20 percent focuses on real-time content production that responds to current events, opposition statements, and emerging social media trends.
Content is distributed across three operational layers, national, regional, and booth-level to ensure consistency and adaptability. National channels handle message creation and digital asset development, regional teams translate and localize material for linguistic and cultural relevance, and booth-level volunteers distribute content through WhatsApp groups and community networks. This tiered flow guarantees that the same political message reaches different demographics in contextually appropriate formats.
Engagement strategy is segmented into three major categories: organic engagement (60 percent), paid amplification (25 percent), and influencer-driven campaigns (15 percent). Organic engagement relies on volunteer interaction, daily posting, and discussion-based mobilization.
Paid engagement uses targeted digital ads to boost visibility among undecided voters. Influencer engagement leverages regional creators and social media personalities to humanize political messages and extend their reach beyond official channels.
Through this integrated approach, the Modi Mitra Digital Army maintains message uniformity while achieving broad, real-time digital saturation. Its combination of structured content planning, localized adaptation, and multi-channel engagement ensures high visibility and sustained voter interaction throughout the campaign cycle.
The ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army follows a structured content and engagement framework designed to maintain high-frequency communication, real-time responsiveness, and localized influence across social and digital platforms. The system combines centralized coordination from the BJP IT Cell headquarters with decentralized volunteer participation, ensuring a rapid, consistent flow of messages from the national level to every booth.
Daily Content Dissemination
Each day, 5 to 10 posts are distributed through hierarchical WhatsApp and Telegram groups, starting from national headquarters and cascading down to state, district, and booth-level teams. These posts include infographics, short videos, and issue-based narratives related to governance, welfare schemes, and regional concerns.
The goal is to maintain message uniformity while allowing contextual flexibility so local teams can adapt national content to their audiences. This rhythm of daily distribution ensures constant voter engagement and prevents message fatigue within digital communities.
Voter Data Collection through the Sakal App
Data collection forms a key component of digital operations. The Sakal App is integrated into the campaign structure to collect real-time information about voters’ preferences, engagement behavior, and geographic clusters.
Field volunteers collect data during door-to-door visits, while digital teams analyze it for segmentation and personalized communication. The continuous feedback loop between data collection and content deployment allows quick recalibration of messaging strategies based on audience response.
Soft Interviews and Controlled Messaging
The IT Cell conducts carefully managed “soft interviews” with ministers and party representatives. These interviews are framed around pre-approved questions that highlight developmental achievements, governance narratives, and leadership credibility.
The conversational tone makes the content appear authentic and relatable, while also keeping control over political messaging. These videos are circulated through digital channels and volunteer groups to subtly influence public perception.
Paid and Unpaid Collaborations
To expand digital reach, the campaign engages both paid and unpaid collaborators. Influencers and micro-creators are compensated at approximately ₹45–50 per post. On a national scale, around 100 influencers are mobilized per campaign cycle.
In addition to paid efforts, thousands of unpaid volunteers contribute content amplification through personal accounts, community forums, and local pages. This hybrid approach maximizes visibility while efficiently managing costs.
Real-Time Trend Hijacking and Hashtag Campaigns
A dedicated digital response unit monitors online trends and triggers immediate campaigns using trending hashtags and event-based narratives. When political, social, or entertainment stories gain traction, the IT Cell crafts quick-response content designed to insert the BJP’s messaging into ongoing digital conversations.
This practice, often called “trend hijacking,” helps sustain visibility, disrupt opposition narratives, and frame national discourse in line with the party’s communication goals.
Operational Effectiveness Metrics
The operational effectiveness of the ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army is measured through quantifiable indicators that track message reach, engagement consistency, and data responsiveness across all organizational levels. The IT Cell evaluates daily performance through metrics such as content circulation rates, volunteer participation levels, WhatsApp group activity, and voter data input via the Sakal App.
Engagement analytics are divided between organic and paid efforts. Organic metrics assess volunteer-driven interactions, repost frequency, and discussion depth within digital communities.
Paid campaign metrics include influencer post reach, cost-per-engagement, and conversion efficiency for targeted voter clusters. The IT Cell also monitors real-time responsiveness, tracking how quickly regional and booth-level teams distribute content after national dispatch.
Data accuracy and feedback integration serve as another performance measure. The Sakal App’s real-time inputs help identify active regions, shifts in voter sentiment, and variations in content performance. Periodic internal audits verify whether communication objectives align with on-ground results.
Together, these metrics create a transparent feedback loop that helps the Modi Mitra network identify underperforming areas, optimize content flow, and strengthen its overall digital command structure for sustained political influence.
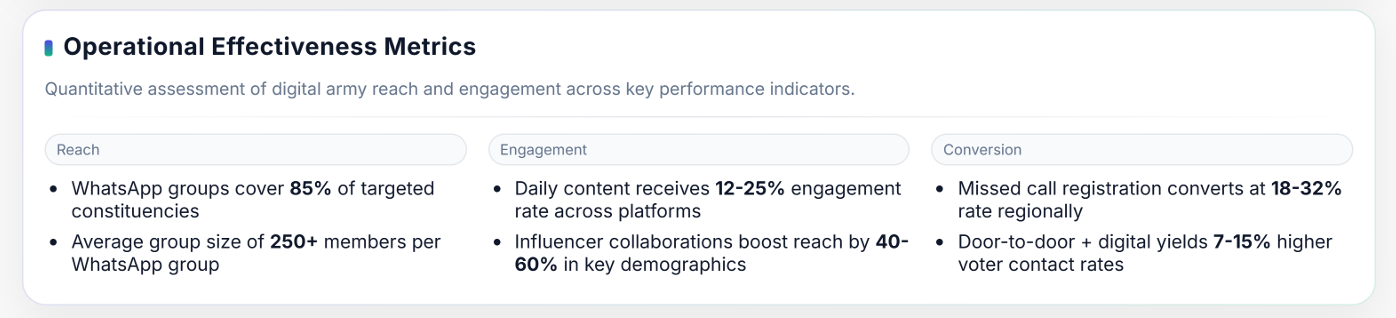
Reach
The reach of the ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army represents one of its strongest operational metrics, driven primarily through a deeply integrated WhatsApp network. Approximately 85 percent of targeted constituencies are covered by structured WhatsApp groups that connect directly with volunteers, influencers, and local voters.
This penetration rate allows near-complete message circulation in real time across both urban and rural constituencies.
Each WhatsApp group typically has over 250 members and functions as a digital micro-community. These groups are not random clusters but strategically organized at the booth and ward levels. Volunteers, local leaders, and regional IT coordinators manage these groups to ensure that every communication from national campaign directives to hyperlocal updates reaches the intended audience without delay or distortion.
The network’s architecture supports both top-down and bottom-up information flow. National headquarters can distribute campaign material, media assets, and real-time alerts within minutes, while booth-level coordinators share voter feedback, grievances, and regional sentiment directly with data teams. This two-way system helps refine political messaging and ensures responsiveness to constituency-level concerns.
By combining vast coverage with tightly managed group hierarchies, the BJP’s IT Cell transforms WhatsApp from a communication platform into a controlled digital infrastructure for voter mobilization, sentiment monitoring, and rapid information deployment. The scale and precision of this model give the Modi Mitra network sustained engagement reach, enabling consistent voter contact across millions of digital touchpoints.
Engagement
Engagement serves as the key indicator of how effectively the ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army converts its digital reach into measurable public interaction. The IT Cell’s engagement model operates through coordinated multi-platform activity, blending planned outreach with adaptive influencer-driven campaigns to sustain visibility and voter sentiment across all target segments.
Platform Performance and Engagement Rates
Daily content distributed via WhatsApp, Facebook, X (Twitter), and regional digital forums averages 12-25% engagement. This figure includes metrics such as shares, comments, link clicks, and forwarded messages.
The variation reflects differences in platform behavior, content type, and demographic focus. Posts that combine local issues with leadership-driven narratives generally record higher engagement than generic campaign messages.
The engagement rate remains consistent because of the Cell’s disciplined scheduling approach; each message is optimized for timing, tone, and content relevance. The digital army prioritizes shareable content formats such as short-form videos, infographics, and quote cards that align with regional voters’ daily consumption habits.
Influence Amplification through Collaborations
Influencer collaborations significantly expand campaign visibility, increasing overall reach by 40-60% among target demographics. These influencers range from regional YouTubers and meme creators to political commentators and administrators of local community groups on social media.
Collaborations are structured in two tiers. The first includes paid influencers who receive fixed compensation per post or campaign cycle. The second tier consists of organic amplifiers, volunteers, supporters, and local leaders who share content without payment but with ideological alignment.
This layered structure creates both credibility and scalability in message dissemination, ensuring that campaign narratives reach audiences through trusted community voices.
Audience Behavior and Response Strategy
The IT Cell tracks engagement in real time to identify which types of content trigger stronger reactions. Issue-based posts related to welfare programs, economic reforms, or leader interactions tend to drive higher engagement among middle-income and youth demographics. Meanwhile, regional content in local languages sustains long-term participation, especially in rural constituencies.
Teams monitor trending discussions and coordinate responses within minutes through WhatsApp and Telegram networks. The feedback gathered from comment sections, group discussions, and message forwards feeds directly into voter sentiment analysis, allowing digital strategists to adjust narrative tone or deploy counter-content against misinformation or opposition campaigns.
Engagement as a Political Tool
Engagement within the Modi Mitra network is not limited to numerical metrics. It functions as a political signal, showing volunteer motivation, voter sentiment shifts, and regional responsiveness to national messaging. Each interaction whether a share, forward, or comment creates a digital footprint that helps the campaign refine its micro-targeting strategy.
By integrating disciplined content flow, influencer outreach, and behavioral analytics, the Modi Mitra Digital Army maintains a self-sustaining engagement ecosystem. This ensures that every message, regardless of its origin or scale, resonates with its intended audience, reinforces loyalty among supporters, and strengthens the perception of an active, citizen-driven digital movement.
Conversion
Conversion within the ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army framework measures how effectively digital outreach translates into active voter participation and registered support. The campaign integrates both online and offline strategies to convert engagement into measurable electoral outcomes, emphasizing data-backed decision-making and consistent follow-up communication.
Missed Call Registration and Digital Onboarding
The missed call registration system serves as the primary entry point for acquiring volunteers and supporters. Each constituency runs localized campaigns encouraging citizens to give a missed call to a dedicated number linked to the Modi Mitra App. This mechanism captures basic contact details and automates onboarding through follow-up SMS, WhatsApp messages, or app-based notifications.
Regionally, the conversion rate from missed calls to confirmed registrations averages 18-32 percent. Urban areas show higher conversion rates due to better digital accessibility, while rural regions rely more on booth-level volunteers to assist with onboarding. These volunteers ensure that every digital lead transitions into an identifiable voter contact within the party’s data infrastructure.
The IT Cell integrates this process with real-time analytics dashboards, allowing state and national teams to track registration trends, volunteer engagement density, and regional response patterns. Continuous monitoring helps refine message targeting and identify districts or demographics with lower conversion efficiency for corrective action.
Hybrid Outreach and Voter Contact Efficiency
The BJP’s IT Cell combines digital outreach with physical mobilization, boosting voter contact rates by 7-15% compared to campaigns that rely solely on door-to-door canvassing. Volunteers use booth-level data to synchronize visits with ongoing digital communication, ensuring that the same voter receives coordinated contact through both physical and online channels.
This hybrid approach improves credibility, as voters perceive consistency between online messages and ground-level interactions. It also minimizes duplication of effort since digital systems automatically record voter responses, enabling volunteers to focus only on undecided or high-priority households.
Behavioral Follow-Up and Retention Strategy
Once a supporter registers digitally, follow-up communication begins within 24 hours through personalized WhatsApp messages, event invitations, and localized updates. The system tracks engagement frequency, identifying users who interact with multiple campaign elements such as surveys, polls, or event RSVPs as high-probability supporters.
Retention is maintained through recurring engagement loops, where digital and physical teams coordinate festival greetings, welfare scheme updates, and leadership messages. These touchpoints keep the campaign visible without overwhelming the voter with repetitive content.
Conversion as a Measurement of Ground Readiness
Conversion data not only reflects digital performance but also signals ground-level readiness. High conversion rates in specific constituencies often correlate with stronger booth management, disciplined volunteer networks, and consistent communication flow between the digital command center and regional cells.
Through sustained coordination between technology, data analytics, and human engagement, the Modi Mitra network transforms voter outreach from passive awareness into measurable political participation. The integration of missed call campaigns, real-time tracking, and hybrid fieldwork ensures that every digital interaction has a traceable impact on voter mobilization and turnout potential.
Regional Deployment Benchmarks
The regional deployment benchmarks of the ‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army outline how the BJP’s IT Cell scales its digital and on-ground operations across diverse states. Each regional cell operates as an independent command unit while maintaining direct coordination with the national headquarters.
This ensures that campaign messaging, content flow, and data-driven voter outreach remain consistent while still adapting to local political and cultural contexts.
Uttar Pradesh leads the deployment network with over 450,000 volunteers and 430,000 WhatsApp groups, forming one of the largest digital mobilization systems in the country. Maharashtra follows with a 300,000-strong volunteer base and a dense regional WhatsApp grid focused on urban engagement and influencer-driven communication.
Himachal Pradesh, though smaller in scale, demonstrates full booth-level penetration through 50,000 volunteers managing around 45,000 WhatsApp groups, ensuring coverage across every assembly segment.
Even smaller regions such as Mandi Town are included in the digital ecosystem, ensuring no constituency is overlooked. Nationally, the IT Cell sustains an average of 2.5 million volunteers and an equivalent number of WhatsApp groups, maintaining a near 1:1 coordination ratio. This structure enables the instant dissemination of campaign materials and real-time data reporting from the ground up.
These benchmarks show a systematic, data-oriented model of political mobilization. Each state’s digital reach directly correlates with its electoral significance, population density, and digital adoption rates. By maintaining these operational standards, the Modi Mitra network achieves both scalability and precision, enabling the party to adapt national strategy to regional realities with measurable efficiency.
The regional deployment benchmarks of the Modi Mitra Digital Army demonstrate how the BJP’s IT Cell scales its outreach strategy through region-specific adaptations, balancing national consistency with localized execution. Each state and region operates within a structured digital network where volunteers, WhatsApp groups, and targeted communication tactics work in coordination to reach voters at the constituency and booth levels.
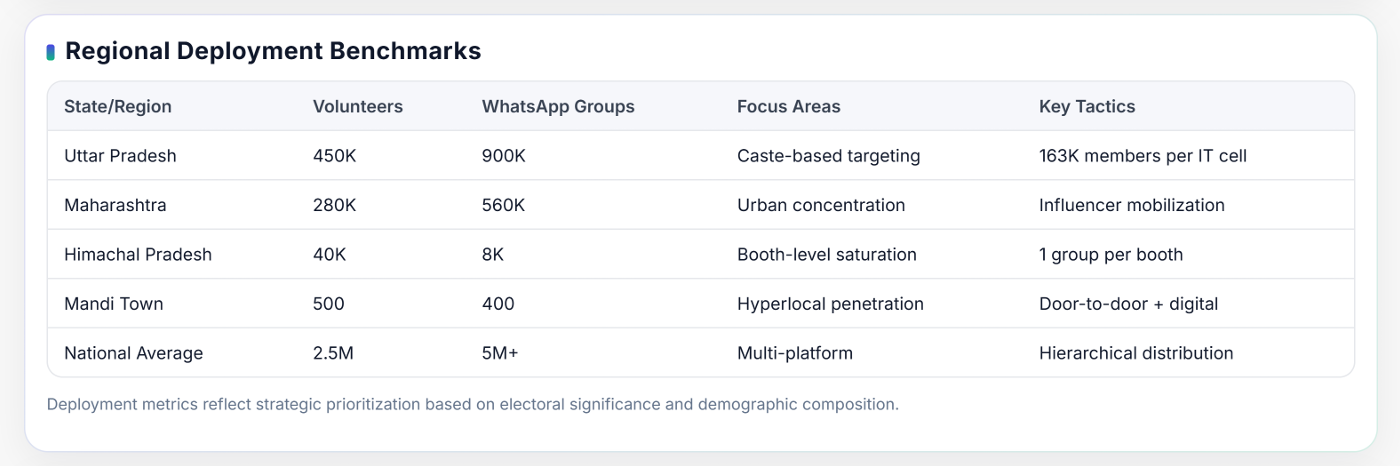
Uttar Pradesh: Scale and Caste-Based Micro-Targeting
Uttar Pradesh represents the most significant operational hub within the Modi Mitra network, with approximately 450,000 volunteers managing 900,000 WhatsApp groups. Each IT Cell maintains an average of 163,000 members organized by caste, locality, and social affiliation.
This segmentation supports precision messaging that connects national policy narratives with community-level identities. The state’s network serves as a testing ground for micro-targeted digital strategies, integrating demographic data with behavioral analytics to strengthen message resonance and turnout mobilization.
Maharashtra: Urban-Focused Digital Penetration
Maharashtra’s 280,000 volunteers and 560,000 WhatsApp groups form a digitally active base primarily concentrated in urban and semi-urban centers such as Mumbai, Pune, and Nagpur. The state’s IT Cell emphasizes influencer mobilization, using content creators, journalists, and community leaders to amplify messages across social media.
Regional WhatsApp and Telegram clusters distribute localized videos, short posts, and leader visuals in Marathi to maintain high visibility across city-based audiences. The urban deployment model in Maharashtra showcases how coordinated influencer outreach can enhance digital credibility and engagement among politically active voters.
Himachal Pradesh: Booth-Level Digital Saturation
Himachal Pradesh operates a smaller but highly structured network of around 40,000 volunteers managing 8,000 WhatsApp groups. The campaign ensures one active group per polling booth, achieving nearly complete digital coverage across constituencies.
The focus here is on booth-level saturation, with consistent message flow from district IT heads to ground volunteers. Each group receives both pre-scheduled content from the state team and hyperlocal updates from regional coordinators, reinforcing uniform message discipline.
Mandi Town: Hyperlocal Coordination Model
Mandi Town demonstrates a concentrated hyperlocal outreach model, with approximately 500 volunteers running 400 WhatsApp groups. The small size of the network allows for precise voter mapping and high response rates. Digital outreach is directly linked to physical contact, combining door-to-door visits with coordinated WhatsApp communication.
This dual approach ensures that every voter receives both personal engagement and digital reinforcement, creating a highly localized cycle of communication and conversion.
National Integration and Hierarchical Coordination
At the national level, the Modi Mitra network sustains over 2.5 million volunteers and more than 5 million WhatsApp groups. The system operates on a hierarchical distribution model that connects the central IT Cell in Delhi with regional, district, and booth-level coordinators.
This vertical structure ensures that national content is localized efficiently and distributed simultaneously across multiple states, maintaining message consistency while allowing regional flexibility.
Each region’s deployment benchmark reflects the BJP IT Cell’s strategic balance between scale, segmentation, and real-time adaptability. The network’s strength lies in its integration of data analytics, local leadership, and consistent volunteer mobilization, creating a cohesive system capable of both mass outreach and precise voter influence.
Modi Mitra Digital Army – Operational Architecture
The operational architecture of the Modi Mitra Digital Army reflects a layered, data-driven communication model that connects national directives to booth-level execution. Managed by the BJP’s central IT Cell, the structure integrates technology, regional coordination, and volunteer networks into a unified system that enables real-time political communication and voter engagement.
At the core, the National Command Center in Delhi coordinates over 150,000 digital workers who manage content pipelines, data analytics, and strategy deployment through the Modi Mitra App. Each state-level IT Cell adapts these directives into local formats, ensuring linguistic and cultural alignment with regional audiences.
The framework extends downward through district, mandal, and booth-level teams that distribute content, monitor engagement, and collect feedback from the ground.
WhatsApp, Telegram, and the Sakal App form the digital backbone of this operation. Over 5 million WhatsApp groups and 2.5 million volunteers participate in structured communication loops, ensuring both horizontal peer engagement and vertical message discipline. Regional coordinators supervise distribution efficiency, while data analytics units track conversion metrics, voter sentiment, and influencer impact.
The architecture’s strength lies in its hybrid model, combining digital precision with on-the-ground mobilization. Each message originates from a centralized source but travels through multiple regional filters before reaching the booth-level voter. This synchronization allows the BJP to maintain consistent national messaging while tailoring outreach to local demographics, achieving both scale and personalization in electoral communication.
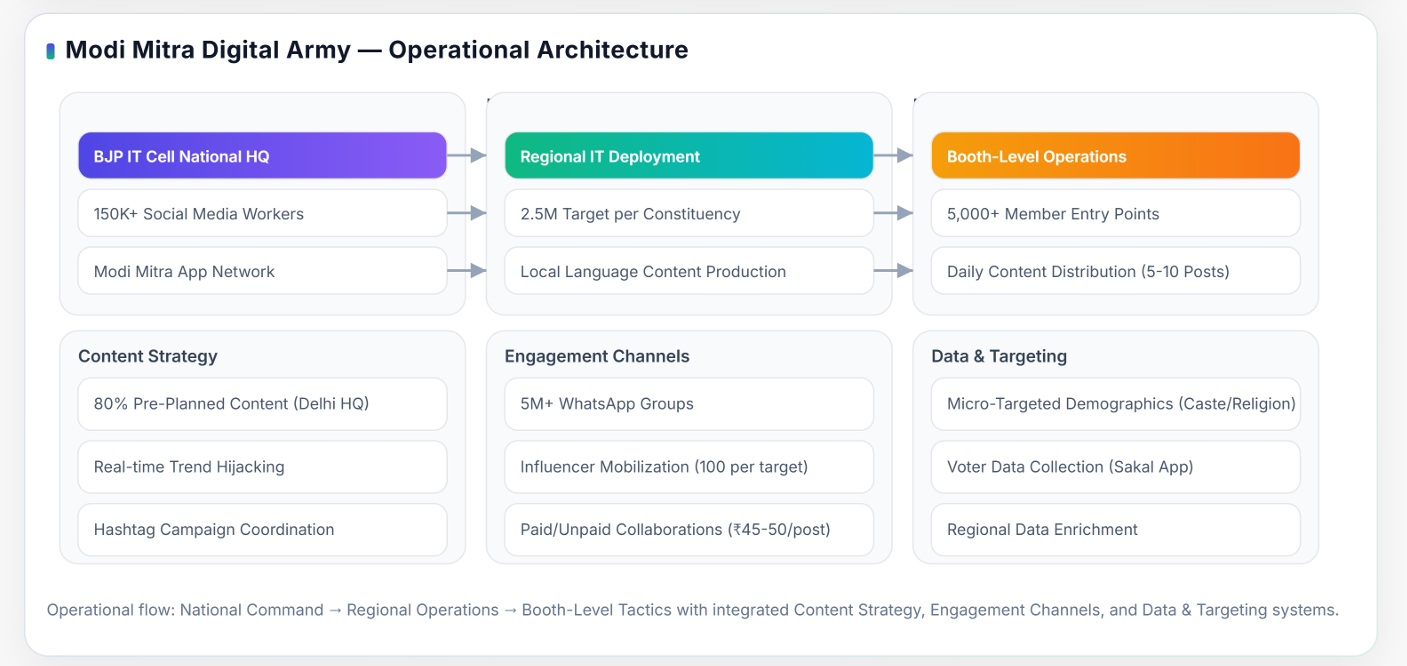
BJP IT Cell National HQ
The BJP IT Cell National Headquarters functions as the nerve center of the Modi Mitra Digital Army, overseeing a vast digital and volunteer network designed for precision-based political communication and voter mobilization.
The headquarters manages both strategic content pipelines and real-time campaign execution across India through centralized coordination and technology-driven systems.
Centralized Command Structure
Operating from Delhi, the National HQ directs approximately 150,000 social media workers who form the backbone of the BJP’s digital communication system. These workers handle content creation, digital monitoring, and narrative management across multiple platforms.
The central command issues daily communication themes, manages crisis response, and ensures message consistency across all state and regional IT Cells.
A dedicated data analytics unit tracks audience behavior, content performance, and sentiment patterns across digital ecosystems. This continuous monitoring allows the HQ to adjust outreach strategies within hours, maintaining relevance and message control.
The digital command also supervises fact-checking operations and counter-narrative mechanisms that respond to misinformation and opposition messaging.
Modi Mitra App Network Integration
The Modi Mitra App connects national-level strategy to regional execution. It serves as a unified communication platform where volunteers receive campaign materials, event updates, and training resources directly from the HQ. The app tracks volunteer activity, measures engagement, and synchronizes booth-level data to the central database.
Through this network, the HQ can launch large-scale campaigns across states within minutes, ensuring uniform message delivery. Every registered volunteer becomes part of a verified digital chain that can amplify posts, conduct surveys, or initiate micro-outreach efforts within their constituency.
Operational Coordination and Workflow
The National HQ functions through vertical divisions dedicated to content, data, media engagement, and outreach logistics. Each team operates on strict timelines, following a structured dissemination workflow. Content is first vetted by central media leads, localized by regional heads, and distributed through state IT Cells before reaching booth-level volunteers.
Daily communication includes campaign schedules, hashtags, multimedia templates, and video scripts shared through the Modi Mitra App and WhatsApp channels. Feedback flows upward through the same network, allowing ground-level insights to influence the next phase of content strategy.
Strategic Role and Impact
The BJP IT Cell National HQ’s primary strength lies in its ability to maintain cohesion across a decentralized network. By integrating digital volunteers, data analytics, and mobile-based coordination tools, the HQ ensures that national messaging is regionally relevant without losing its ideological coherence.
This structure transforms political communication into a continuous feedback loop, in which every volunteer from national command to booth level contributes to data-driven campaign refinement and voter engagement.
Through its 150,000-member social media workforce and Modi Mitra App ecosystem, the National HQ enables the BJP to sustain a 24/7 digital presence, coordinate millions of interactions daily, and execute political campaigns with unmatched operational speed and message discipline.
Regional IT Deployment
The regional IT deployment of the Modi Mitra Digital Army represents the operational layer where national strategy translates into constituency-level execution. It integrates digital coordination, volunteer management, and localized messaging to ensure uniform outreach across diverse linguistic and cultural regions.
Each constituency operates under measurable targets and is supported by a structured digital infrastructure managed through the Modi Mitra App and WhatsApp network.
Scale and Reach Across Constituencies
Each constituency is assigned a deployment target of approximately 2.5 million digital touchpoints, combining volunteer interactions, social media reach, and voter engagement data. Regional IT Cells monitor these targets through real-time dashboards that track message dissemination, volunteer activity, and voter responses.
The system’s scale allows simultaneous content delivery to millions while maintaining precision through micro-segmentation at the booth level.
Regional coordinators oversee multiple constituencies, ensuring that digital and on-ground operations progress in parallel. Each coordinator supervises volunteer teams responsible for managing WhatsApp groups, Telegram channels, and localized content dissemination. This hierarchical yet flexible structure ensures high penetration in both urban and rural areas.
Local Language Content Production
Language adaptation is central to the regional deployment strategy. Each state-level IT Cell manages content translation, voice-over recording, and subtitling in local dialects to align communication with regional sentiment. The content team produces videos, infographics, and posts that reflect local political narratives, cultural references, and community priorities.
By creating content in local languages, the network strengthens emotional connection and message authenticity. Regional content is reviewed by local media heads before release to ensure accuracy and consistency with the national communication framework. This process helps minimize distortion and reinforces ideological cohesion across multiple linguistic zones.
Coordination and Execution Framework
The regional IT deployment follows a clear command and reporting system. State IT heads receive daily content from the national command center, adapt it to the region, and distribute it through district coordinators. Booth-level volunteers then share this content across WhatsApp groups, local pages, and voter circles.
To maintain engagement and responsiveness, each region integrates automated messaging tools and data tracking through the Modi Mitra App. The app records activity metrics, including the number of shares, group interactions, and feedback received. These insights help refine regional communication strategies and resource allocation.
Impact on Ground-Level Mobilization
This regional structure ensures that every message produced nationally is contextually relevant locally. The dual integration of digital messaging and local language content improves message retention, trust, and conversion rates among voters.
As a result, regional IT deployments act as both amplifiers and validators of the national narrative, making them a critical operational link in the BJP’s digital and electoral ecosystem.
Booth-Level Operations
The booth-level operations of the Modi Mitra Digital Army serve as the foundation of its micro-targeted digital and field network. This structure connects the national communication strategy to the smallest electoral units, enabling precise voter outreach and consistent message delivery.
With over 5,000 member entry points, each booth acts as a digital and physical extension of the party’s broader campaign framework.
Structural Organization and Network Integration
Each booth operates as a local command hub that integrates both digital and ground-level outreach. Volunteers at this level manage WhatsApp groups, maintain voter lists, and conduct community engagement activities. These entry points ensure that the campaign reaches every neighborhood, polling area, and social cluster within a constituency.
Booth-level leaders coordinate directly with regional IT Cells and district command centers, reporting daily engagement metrics and feedback through the Modi Mitra App. This structure allows the central command to monitor communication flow and voter response in real time, ensuring no constituency segment remains underrepresented in the digital campaign.
Daily Content Distribution and Messaging Discipline
Each booth-level team distributes 5-10 pieces of content daily, sourced from the national and regional content pipelines. This includes videos, infographics, local news updates, and issue-based messages tailored to community interests. Volunteers ensure timely distribution across WhatsApp groups, Telegram channels, and regional social media pages, reinforcing message consistency across the network.
The content follows a layered distribution system: national messages frame the overarching narrative, regional adaptations address local sentiments, and booth-level versions personalize the appeal using vernacular language, imagery, and locally relevant examples. This daily rhythm sustains audience engagement and keeps the party’s messaging visible and continuous.
Volunteer Coordination and Data Reporting
Each booth network includes designated coordinators who manage the digital volunteers and field operatives. Volunteers gather voter data, monitor local discourse, and report emerging trends through the Modi Mitra App. This upward data flow supports analytics-driven decision-making at higher command levels, ensuring rapid response to evolving public sentiment or misinformation.
Participation levels, content distribution reach, and engagement rates within assigned areas measure performance. Coordinators conduct brief daily meetings to assess outreach efficiency and plan the next communication cycle.
Role in Voter Mobilization
Booth-level operations are not limited to digital activity. They serve as the bridge between online engagement and on-the-ground action. Volunteers organize small community meetings, conduct door-to-door visits, and manage phone or IVR-based voter contact programs. This hybrid structure improves voter awareness, issue recall, and turnout motivation.
Through disciplined execution, localized content delivery, and structured coordination, booth-level operations convert national messaging into actionable voter interaction. This bottom-up model enables the Modi Mitra Digital Army to maintain both scale and precision, ensuring that every booth becomes a node of influence within the larger electoral network.
Content Strategy
The content strategy of the Modi Mitra Digital Army combines centralized planning with agile real-time adaptation to control narratives, maintain message consistency, and engage voters across digital platforms. The BJP’s IT Cell, operating from the Delhi HQ, manages approximately 80 percent of planned content, leaving the remaining 20 percent for reactive campaigns designed to capitalize on emerging trends. This hybrid model ensures both discipline in communication and flexibility in response.
Pre-Planned Content from Delhi HQ
The majority of the content originates from the BJP’s central IT Cell in Delhi. This content includes campaign videos, issue-based graphics, slogans, leader speeches, and data-driven narratives synchronized with the party’s national agenda.
Pre-planned materials are approved through an internal review chain involving the central communication team, digital war room analysts, and regional IT heads before deployment.
Each piece is designed for scalability, with templates localized for regional use through language adaptation and contextual imagery. Daily schedules specify the time and sequence of dissemination across hierarchical groups from national pages to booth-level WhatsApp networks. This ensures simultaneous nationwide amplification of the same message.
The advantage of this system lies in maintaining ideological consistency and controlling the flow of messages. The Delhi HQ’s pre-planned content calendar aligns with key political events, rallies, policy announcements, and targeted constituency campaigns, guaranteeing a continuous communication cycle that sustains audience engagement.
Real-Time Trend Hijacking
Beyond pre-planned messaging, the digital command center monitors trending topics across social media to identify opportunities for real-time intervention. When political, social, or cultural events gain traction online, regional and national IT teams rapidly craft responses using pre-approved templates and talking points.
Trend hijacking serves two purposes: reinforcing the party’s visibility during primary news cycles and reframing debates in a politically advantageous manner. Dedicated monitoring units use sentiment analysis tools to identify viral moments within minutes and direct volunteers to engage using coordinated responses.
This real-time agility allows the digital army to dominate narratives, ensuring that the party’s perspective remains prominent across trending hashtags, news comments, and viral conversations.
Hashtag Campaign Coordination
Hashtags serve as digital anchors for visibility and message tracking. Every campaign, whether national or regional, is assigned specific hashtags that volunteers use to push content simultaneously across platforms like X (Twitter), Instagram, and Koo.
Central command teams coordinate hashtag launches by pre-scheduling times to ensure synchronized surges in online traffic. This approach triggers algorithmic boosts, pushing the campaign higher in platform feeds and trending sections. Once active, regional and booth-level IT cells amplify hashtags within local groups, encouraging members to comment, repost, and quote content to sustain reach.
To maintain momentum, influencer networks and paid collaborations reinforce the campaign through content partnerships. Daily performance is tracked through engagement dashboards measuring reach, impressions, and post frequency, ensuring measurable accountability across the hierarchy.
Integration and Strategic Impact
The integration of structured pre-planning and real-time responsiveness creates a continuous content flow that can dominate digital conversations. The central command’s planning ensures coherence, while regional adaptability and trend hijacking inject freshness into the daily narrative.
This system transforms content distribution from one-way messaging into a coordinated information ecosystem, where every tweet, video, and post, whether centrally produced or locally adapted, serves a defined political function.
By merging premeditated consistency with tactical spontaneity, the Modi Mitra Digital Army sustains digital dominance in India’s multilingual, fast-moving political media environment.
Engagement Channels
The engagement framework of the Modi Mitra Digital Army combines large-scale digital infrastructure with micro-level influencer and volunteer networks to ensure consistent communication and voter mobilization.
It integrates over 5 million WhatsApp groups, structured influencer coordination, and mixed paid–unpaid collaborations to create a sustained flow of political messaging across demographics and regions.
WhatsApp Network as the Core Distribution Layer
The backbone of the engagement strategy is a vast WhatsApp ecosystem that connects national command structures with local voters. More than 5 million groups function as communication clusters, each containing an average of 250 to 300 members. These groups operate in a hierarchical format, linking national and state IT Cells with booth-level coordinators who distribute content daily.
This structure ensures that every voter segment from metropolitan residents to rural communities receives consistent messaging. Information dissemination follows a top-down flow, starting at Delhi HQ, then to state digital units, and finally to district and booth-level groups. Volunteers manage group engagement by encouraging discussion, sharing visuals, and collecting local feedback to inform real-time strategy adjustments.
The advantage of this decentralized model lies in its scalability and resilience. Even when one node or group faces restrictions, thousands of parallel channels continue to operate, ensuring message continuity without disruption.
Influencer Mobilization
Influencer coordination strengthens reach and relatability within specific social and demographic categories. Each principal campaign target includes approximately 100 influencers selected for their digital presence, regional language fluency, and audience credibility. These influencers range from micro-content creators with 10,000 followers to mid-tier personalities with regional media visibility.
They participate in coordinated campaigns aligned with the party’s messaging calendar, using shared content kits prepared by the digital command team. Their posts amplify hashtags, humanize political narratives, and engage audiences through issue-based storytelling, memes, or commentary.
Performance tracking is done through digital dashboards that monitor engagement metrics, such as shares, comments, and impressions. Influencers who perform consistently are integrated into long-term collaborations, allowing message reinforcement across multiple election cycles.
Paid and Unpaid Collaborations
The engagement system blends volunteer-driven outreach with paid collaborations to maintain momentum and reliability. Paid partnerships average between ₹45–₹50 per post for micro-influencers, ensuring scalable yet cost-efficient visibility. Unpaid volunteers, including party supporters and grassroots workers, complement this effort by organically distributing content within their networks.
The distinction between paid and unpaid collaboration allows flexibility. Paid campaigns guarantee predictable engagement spikes, while unpaid networks sustain daily discourse and authenticity. Local volunteers, in particular, contribute credibility by adapting messages to their regional context and language, creating emotional proximity with local audiences.
Integration and Feedback Mechanisms
All engagement channels operate within a unified monitoring and reporting structure managed through the Modi Mitra App and internal dashboards. These tools collect metrics on post frequency, group activity, influencer performance, and regional response rates.
Weekly evaluations help the national IT Cell identify high-performing clusters and optimize resources toward regions with measurable impact. Data-driven adjustments ensure that engagement remains dynamic, relevant, and strategically aligned with electoral timelines.
Strategic Impact
The combination of mass digital connectivity, influencer amplification, and localized volunteer energy creates a multilayered communication network that balances scale with personalization. This engagement infrastructure allows the Modi Mitra Digital Army to saturate information spaces rapidly, maintain control over political narratives, and translate digital reach into measurable voter influence.
By integrating structured WhatsApp networks, influencer ecosystems, and adaptive collaboration models, the operation achieves its central goal: sustained digital presence across India’s linguistic, regional, and demographic spectrum with minimal message dilution.
Data and Targeting
The Modi Mitra Digital Army operates on a data-driven framework that integrates demographic profiling, voter analytics, and regional data refinement to optimize campaign targeting.
Its structure blends large-scale centralized data collection with local enrichment processes, allowing the BJP’s IT Cell to micro-target voters based on caste, religion, geography, and behavioral indicators. This hybrid system enables precision outreach and narrative customization across constituencies.
Micro-Targeted Demographics
The digital command center classifies voter segments into distinct demographic and socio-political categories. These include caste affiliations, religious identities, occupational clusters, and regional communities. Each category receives tailored messaging that reflects local priorities, cultural nuances, and political sentiment.
For example, caste-based targeting focuses on communities that influence electoral outcomes within a constituency. Messaging emphasizes welfare schemes, leadership representation, and cultural alignment. Religion-based segmentation prioritizes identity-linked appeals, emphasizing national pride, security, and community welfare.
This segmentation extends to gender, age, and profession, enabling targeted outreach to farmers, youth, women, and small business owners. Each group receives specific communication through videos, infographics, and testimonials designed to align with their emotional and social priorities.
By combining demographic data with behavioral insights from social media interactions and booth-level reports, the IT Cell creates an adaptable targeting grid that evolves with voter behavior.
Voter Data Collection through the Sakal App
The Sakal App functions as a central voter intelligence system. Volunteers and booth-level coordinators use the app to record household-level voter data, including demographic details, voting history, and issue preferences.
This information is verified through cross-referencing with electoral rolls and ground-level surveys. The app’s interface allows real-time data syncing, ensuring continuous updates from volunteers across states. It also includes modules for tracking digital engagement, event participation, and sentiment trends.
The integration of Sakal App data with WhatsApp network analytics creates a complete picture of each constituency’s voter composition. This enables regional IT cells to plan localized outreach campaigns and mobilize resources efficiently in advance of election cycles.
Data protection protocols and hierarchical access controls ensure that sensitive voter data remains confined to authorized personnel. The system prioritizes accuracy and reliability, as outdated or duplicated data can distort targeting outcomes.
Regional Data Enrichment
Regional IT Cells refine central data inputs by adding contextual information gathered from fieldwork, surveys, and social media listening. This enrichment process includes identifying key influencers, mapping linguistic variations, and tracking district-level issues.
Local volunteers contribute updates about shifting voter sentiment, regional controversies, or socio-economic changes affecting specific demographics. These inputs help adjust messaging tone, timing, and language, ensuring that national narratives resonate with local audiences.
Regional enrichment also includes cross-verification of caste-community boundaries and religious distributions, particularly in constituencies with mixed populations. By analyzing variations in issue sensitivity across districts, the digital command can dynamically adjust campaign themes.
Data visualization dashboards consolidate this information for central review, allowing decision-makers to compare voter trends and engagement levels across regions.
Strategic Outcomes
The integration of demographic targeting, real-time voter data collection, and regional enrichment transforms the Modi Mitra network into a precision campaign engine. Each digital action, whether a WhatsApp message, influencer post, or short video, targets a defined audience segment with measurable intent.
This data-driven approach reduces message wastage, enhances voter engagement, and improves campaign efficiency. By linking demographic insights with localized intelligence, the BJP’s IT Cell ensures that its communication remains both broad in reach and granular in impact, forming the operational core of the Modi Mitra Digital Army’s micro-targeted outreach model.
Operational Security and Compliance
The Modi Mitra Digital Army maintains a strict operational security framework to protect its digital assets, data pipelines, and communication channels. All volunteer and IT Cell operations function under a layered compliance model that prioritizes data integrity, controlled access, and message discipline. Each participant is vetted and assigned role-based permissions to ensure accountability and prevent data misuse.
Data collected through the Sakal App and other digital tools is encrypted and stored on secure internal servers. Regional teams follow defined protocols for information transfer, ensuring that voter data, communication logs, and performance reports remain protected from external access. WhatsApp groups and digital dashboards are monitored by administrators who oversee content sharing and detect unauthorized activity or data leaks.
Compliance mechanisms are enforced through continuous monitoring and internal audits. The central IT Cell in Delhi issues periodic directives outlining ethical guidelines, content boundaries, and data usage norms. This includes adherence to local election communication laws and platform-specific community standards: violations or unauthorized messaging trigger immediate suspension from network activities.
Operational secrecy is essential to preserving campaign strategy and maintaining narrative control. The combination of controlled data access, encrypted infrastructure, and standardized compliance procedures allows the Modi Mitra Digital Army to sustain nationwide coordination while minimizing operational risk.
The Modi Mitra Digital Army operates under a structured security and compliance framework designed to maintain message discipline, protect voter data, and ensure adherence to digital communication laws. Its operational systems combine centralized oversight with regional accountability, ensuring that content, data, and engagement remain secure and verifiable at every stage of distribution.
Content Governance
The central IT Cell in Delhi oversees all digital communication through a mandatory pre-approval process. Around 80 percent of distributed content originates from headquarters, ensuring consistency in tone, visuals, and language.
Each piece undergoes review to verify factual accuracy, political alignment, and compliance with brand-safe messaging guidelines.
Regional digital teams receive these assets through the internal content management pipeline and adapt them to local contexts without altering the core message. This pre-clearance model prevents misinformation, enforces quality control, and ensures uniformity across millions of WhatsApp groups and social media posts.
Volunteers and influencers follow standardized briefing documents to avoid unauthorized or speculative messaging.
Data Protection
Data protection protocols form the foundation of the Modi Mitra digital infrastructure. The Sakal App, integrated into the voter outreach system, handles voter records through encrypted channels. Only authorized personnel with verified credentials can access or edit the data.
Each regional team is responsible for maintaining local voter databases that complement the central repository. Regular sync operations ensure accuracy, while automated verification eliminates duplicate or outdated entries. Sensitive demographic data, such as caste, religion, and household details, remain compartmentalized to prevent misuse.
Access is restricted through layered authentication systems, and all activity is logged and timestamped for accountability. Volunteers are trained in digital hygiene and privacy awareness to ensure voter information is handled responsibly.
Platform Compliance
The Modi Mitra network strictly adheres to digital platform rules to avoid content takedowns or legal complications. WhatsApp group structures adhere to the official group size and broadcast limits, ensuring compliance with the platform’s anti-spam regulations.
Regional communication coordinators monitor content flow to prevent mass forwarding or automated spam-like activity, which could trigger moderation or suspension. On platforms like X (Twitter), Facebook, and Instagram, content teams adhere to community guidelines, election commission directives, and paid promotion disclosures.
The IT Cell periodically updates digital compliance checklists aligned with platform policy changes to prevent account suspensions and maintain credibility during election cycles.
Audit Trails
Every piece of distributed content and engagement activity is recorded through immutable audit logs maintained in internal dashboards. These records document message origin, distribution path, and interaction metrics.
Audit trails allow supervisors to trace campaign effectiveness and identify irregularities, such as unauthorized postings or unverified messages. Weekly performance audits assess engagement rates and verify that each content node operates within approved parameters.
This transparent tracking system ensures operational accountability from headquarters to booth-level workers. It also helps detect manipulation, misinformation, or infiltration attempts, allowing rapid corrective action.
Conclusion
The Modi Mitra Digital Army is among the most systematically organized digital political networks in India. Its structure combines centralized command, regional customization, and data-driven precision to ensure message consistency, voter engagement, and operational discipline.
The network’s strength lies in its layered hierarchy from the BJP’s national IT Cell in Delhi to state, district, and booth-level teams, each performing specialized roles in content creation, voter outreach, and analytics. With over five million WhatsApp groups and extensive volunteer participation, the system achieves near-total penetration across constituencies.
Operational efficiency is maintained through a mix of automation, human oversight, and localized intelligence. Content flows from a centralized source, where 80 percent of material undergoes pre-approval for factual accuracy and brand alignment. Regional IT Cells adapt this content linguistically and contextually, ensuring cultural relevance without distorting the message.
The integration of the Sakal App demonstrates the campaign’s reliance on technology for voter data management. This app enables real-time data collection, cross-verification, and micro-targeting based on caste, religion, and behavioral insights. Encrypted infrastructure and controlled access ensure that sensitive voter data remains secure and compliant with privacy norms.
At the engagement level, influencers, coordinated hashtag campaigns, and real-time trend hijacking enhance digital visibility. Paid and unpaid collaborations further amplify reach within strategic demographics, maintaining a constant narrative presence online.
Security and compliance form the operational backbone of the network. Defined governance mechanisms, strict data protocols, and immutable audit trails ensure accountability, legal conformity, and protection against misinformation or external interference.
Overall, the Modi Mitra Digital Army operates as a hybrid of technology, organization, and psychology. Its success stems from unifying mass communication with micro-level personalization, creating a self-sustaining, adaptive digital ecosystem that mirrors the scale and precision of a national political machine.
‘Modi Mitra’ Digital Army: BJP’s IT Cell Micro-Targeted Outreach Network – FAQs
What Is the Modi Mitra Digital Army?
The Modi Mitra Digital Army is an organized digital network managed by the BJP’s National IT Cell. It coordinates social media communication, voter engagement, and data-driven outreach across India.
How Is the Digital Army Structured?
The network operates in a hierarchical format, starting from the BJP IT Cell National Headquarters in Delhi and extending to state, district, and booth-level teams.
How Many Volunteers Are Part of This Network?
Over 150,000 social media workers are connected nationally, with millions of regional volunteers operating through the Modi Mitra App and local IT Cells.
What Is the Purpose of the Modi Mitra App?
The Modi Mitra App manages volunteer registration, training, and real-time coordination, enabling two-way communication between the central IT Cell and grassroots teams.
How Does Regional Deployment Work?
Each constituency manages around 2.5 million target voters, with localized content creation in regional languages to improve message relevance and voter connection.
What Is the Role of Booth-Level Teams?
Booth-level volunteers distribute daily digital content, conduct door-to-door outreach, and collect voter data using structured digital and field systems.
How Is Content Created and Distributed?
Nearly 80 percent of content originates from the Delhi headquarters, reviewed for accuracy and messaging consistency before regional adaptation and dissemination.
What Types of Content Are Shared Daily?
Volunteers distribute 5–10 posts per day that include campaign updates, issue-based videos, local achievements, and calls to action aligned with the BJP’s communication goals.
How Does the Network Ensure Message Discipline?
All content undergoes pre-approval, with regional teams required to use templates and standardized language to prevent misinformation or deviation from official narratives.
What Is the Role of Data in This Operation?
Data collection and targeting are central to operations. Voter data from the Sakal App and regional sources help the network segment audiences based on caste, religion, and locality.
How Is Voter Data Protected?
Voter records are encrypted, stored on secure internal servers, and accessed only by authorized personnel with verified credentials.
How Does the Network Handle Regional Language Communication?
Local IT Cells translate, voice-over, or recreate content in regional languages to match local dialects and cultural nuances while preserving the original message.
What Are the Key Engagement Channels?
The main communication channels are WhatsApp groups, regional influencer collaborations, social media posts, and interactive online campaigns.
How Large Is the WhatsApp Outreach?
The network operates more than 5 million WhatsApp groups, covering nearly 85 percent of targeted constituencies with an average of 250 members per group.
What Role Do Influencers Play?
Around 100 influencers per national target are engaged through both paid and unpaid collaborations, typically earning ₹45–50 per post.
What Are the Engagement Metrics?
Daily content averages a 12–25 percent engagement rate across platforms, with influencer involvement boosting visibility by up to 60 percent.
How Are Conversions Measured?
Missed-call registration campaigns convert at 18–32 percent, while door-to-door combined with digital outreach increases voter contact by up to 15 percent.
What Security Measures Are in Place?
Operations use encryption, access controls, and audit logs. Immutable records track content flow and engagement to maintain transparency and accountability.
How Does the Network Ensure Compliance With Platform Rules?
Teams follow WhatsApp group limits, social media policies, and Election Commission guidelines to avoid account bans and regulatory breaches.
Why Is Operational Security Critical to the Modi Mitra Model?
Security ensures message integrity, prevents data leaks, and protects the network from misinformation, infiltration, or external manipulation during high-stakes campaigns.











