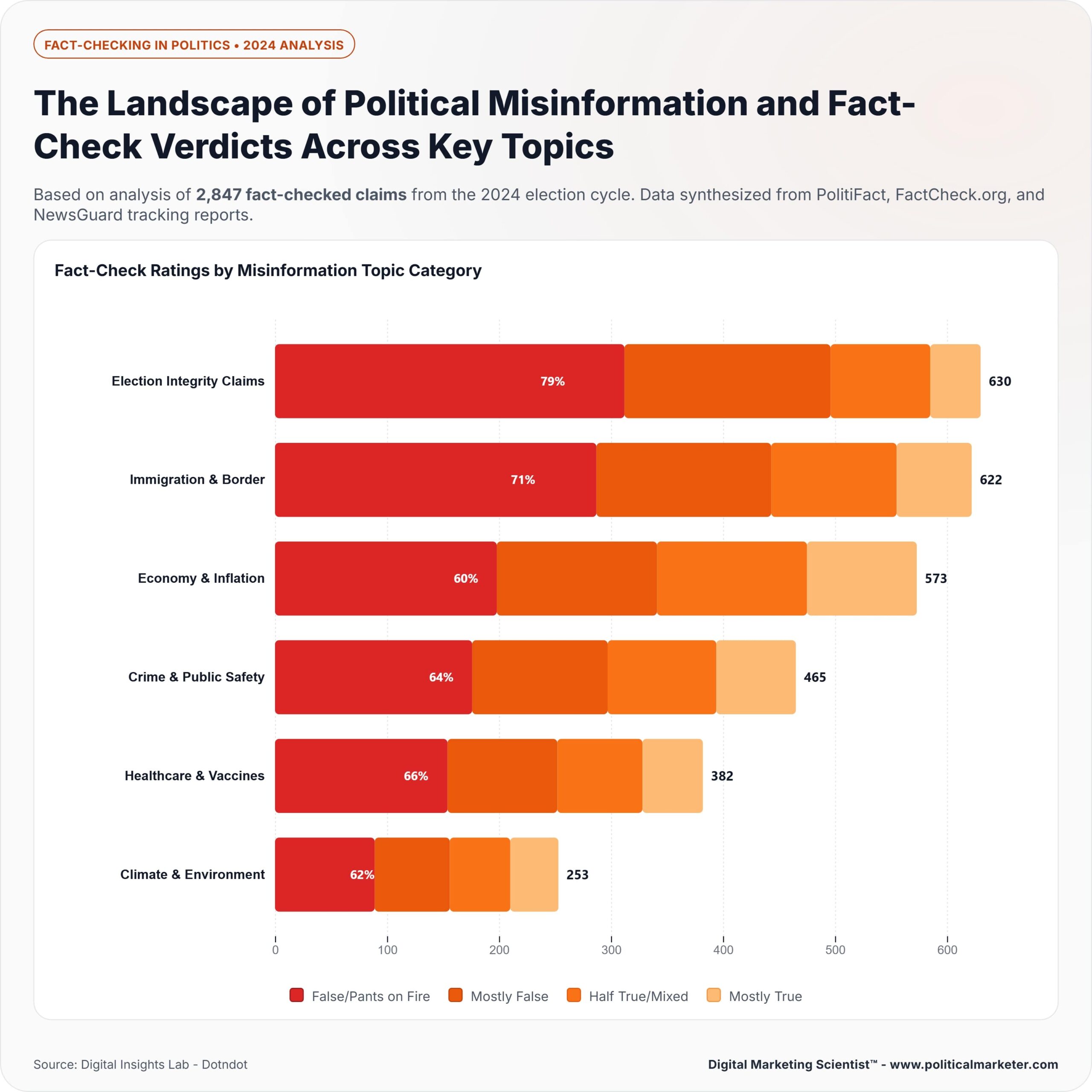
Fact-checking in politics has become a crucial safeguard in an era where misinformation, half-truths, and propaganda can spread instantly across digital platforms. It involves the systematic verification of political statements, campaign promises, government policies, and media narratives to determine their accuracy. By evaluating evidence, consulting reliable sources, and applying transparent methodologies, fact-checking organizations enable citizens to distinguish truth from manipulation. This process is vital for maintaining democratic accountability, as voters depend on accurate information to make informed decisions.
One of the core functions of political fact-checking is to counteract misinformation during election campaigns. Politicians often employ persuasive rhetoric or exaggerations to appeal to public sentiment, but unchecked claims can mislead voters. Fact-checking serves as a corrective tool, exposing falsehoods and clarifying context so that the electorate is not swayed by misinformation. Real-time fact-checking during debates and rallies has further underscored its importance, providing immediate verification that prevents the dissemination of misleading narratives.
The rise of social media has made fact-checking even more essential. Platforms like X (formerly Twitter), Facebook, and WhatsApp can amplify political claims to millions within minutes, creating an environment where misinformation travels faster than corrections.
Despite its importance, political fact-checking faces significant challenges. Partisan bias accusations often undermine the credibility of fact-checking organizations, as political parties may dispute unfavorable findings. Additionally, the rapid speed of information dissemination makes it difficult to provide timely corrections before false claims influence public opinion. Cultural, linguistic, and regional variations also create barriers, especially in countries with diverse populations and multiple political narratives.
The impact of fact-checking on political trust is a subject of ongoing debate. While some research suggests that exposing false claims can reduce belief in misinformation, others argue that deeply polarized voters may dismiss fact-checks that contradict their partisan leanings. Nevertheless, the presence of independent, transparent fact-checking entities contributes to a healthier political ecosystem by holding leaders accountable and encouraging greater scrutiny of public communication.
Looking forward, fact-checking in politics is expected to become even more integrated with technology. AI-driven tools for real-time claim verification, blockchain for transparent data trails, and cross-border collaborations among fact-checking organizations could strengthen accuracy and speed. At the same time, public education campaigns will play a vital role in teaching citizens how to evaluate information and recognize trustworthy sources critically. Ultimately, fact-checking is not just about correcting falsehoods; it is about empowering citizens, reinforcing democratic norms, and building resilience against the manipulation of truth in political discourse.
How Does Political Fact-Checking Protect Voters From Misinformation
Political fact-checking protects voters by verifying the accuracy of claims made by politicians, parties, and media outlets. It helps prevent the spread of false narratives that can mislead public opinion, especially during elections. By analyzing speeches, campaign promises, advertisements, and viral social media content, fact-checkers provide evidence-based insights that enable citizens to make informed choices. This process not only curbs misinformation but also strengthens democratic accountability by holding leaders responsible for their words and actions.
How Political Fact-Checking Protects Voters
Political fact-checking plays a direct role in protecting voters from misinformation by verifying the claims made by politicians, parties, and campaign groups. During election cycles, candidates often make sweeping statements about economic growth, welfare programs, or past achievements. Fact-checkers evaluate these statements against credible data, research, and public records to verify their accuracy. When false or exaggerated claims appear, fact-checkers correct them promptly, allowing you to make informed decisions based on accurate information.
Ensuring Accountability in Campaigns
Campaign rhetoric often simplifies complex policies, which makes it easier for false narratives to gain traction. Fact-checking forces politicians to remain accountable because their words are subject to independent verification and scrutiny. For voters, this means you are less likely to be misled by promises that sound appealing but lack evidence. In high-stakes moments, such as live debates, real-time fact-checking provides immediate corrections, reducing the risk of misinformation spreading unchecked.
Combating Misinformation on Social Media
Social media platforms allow false political claims to reach millions in minutes. Political actors may exploit this speed to manipulate public opinion. Fact-checkers monitor these platforms, flagging misleading content and sharing evidence-based corrections. By doing so, they limit the influence of viral misinformation campaigns and help you distinguish between authentic political communication and fabricated stories.
The Role of Technology in Fact-Checking
Modern fact-checking relies on technology to keep up with the volume of information. These technologies also detect manipulated images, edited videos, and deepfakes. By integrating human judgment with automated detection, fact-checking organizations increase both speed and accuracy.
Challenges in Building Trust
Despite its value, fact-checking faces resistance. Political groups often reject unfavorable findings and label them as biased. In highly polarized environments, some voters ignore corrections that conflict with their party loyalty. For fact-checking to remain effective, organizations must demonstrate transparency in their methods and maintain independence from political influence. Clear communication of evidence helps build credibility with the public.
Impact on Voter Decision-Making
When fact-checking is effective, it enhances democratic participation. Voters who have access to verified information are less vulnerable to manipulation and more likely to evaluate candidates on their actual records. This helps shift the focus of campaigns from emotional persuasion to evidence-based discussion. By filtering out falsehoods, fact-checking provides a stronger foundation for selecting leaders who reflect your interests and values.
Future of Political Fact-Checking
The need for political fact-checking will only increase as digital campaigning continues to evolve. The next stage involves stronger collaboration between media outlets, academic researchers, and independent organizations. Public education also matters because voters must learn how to recognize misleading claims and seek reliable sources. Combined with advanced tools, these efforts ensure that fact-checking remains a vital defense against political misinformation.
What Role Does Fact-Checking Play in Modern Election Campaigns
Fact-checking plays a central role in modern election campaigns by verifying the accuracy of political statements, advertisements, and debate performances. It prevents candidates from misleading voters with false promises or exaggerated achievements. Independent fact-checking organizations examine evidence, compare claims with official data, and provide corrections that help you see beyond campaign rhetoric. This process promotes accountability, reduces the spread of misinformation, and ensures that election decisions are based on facts rather than manipulation.
Holding Candidates Accountable
Fact-checking holds political candidates accountable during campaigns. Every claim about policy successes, economic growth, or government performance is subject to review by independent organizations. When a candidate makes an exaggerated or false statement, fact-checkers investigate the evidence and publish corrections. This accountability discourages the spread of misleading rhetoric and helps you focus on verified facts rather than political spin.
Verifying Campaign Promises
Election campaigns often rely on promises that appeal to voter emotions. Fact-checkers assess whether these promises are realistic and supported by evidence. For example, if a candidate pledges to deliver free healthcare, fact-checking assesses the economic feasibility and reviews their legislative history. By comparing claims with actual data, fact-checking helps you judge whether candidates have the capacity and credibility to deliver on their promises.
Protecting Voters From Manipulation
Political campaigns are increasingly using targeted messaging, particularly on social media. Some ads or speeches are designed to exploit fears or spread half-truths. Fact-checking interrupts this cycle by exposing misleading narratives before they gain traction. It prevents false claims from shaping your opinion and ensures that you base your decisions on verified information.
Role in Political Debates
Live debates are moments where candidates make bold claims under pressure. Real-time fact-checking during these events has become essential. Media outlets and fact-checking teams quickly verify statistics, policy references, and accusations. By publishing corrections during or immediately after debates, fact-checkers limit the influence of falsehoods and give you accurate context while the discussion is still fresh.
Monitoring Political Advertising
Election advertising is another channel where misinformation spreads. Candidates and parties spend large sums on ads that may exaggerate achievements or attack opponents with distortions. Fact-checkers review these advertisements and issue reports that clarify misleading claims. This oversight makes campaign advertising more transparent and reduces the effectiveness of manipulative tactics.
Combating Social Media Disinformation
False claims can reach millions within minutes, often faster than corrections can be issued. They use both technology and human review to ensure rapid responses. This process mitigates the long-term impact of false narratives in online spaces where voters spend a significant portion of their time.
Building Voter Confidence
Fact-checking not only corrects false claims but also strengthens your confidence in the electoral process. When you know that independent reviews exist, you are less likely to feel manipulated by political rhetoric. This trust supports more informed voting behavior, ensuring that election results reflect decisions based on facts rather than propaganda.
Challenges in Political Fact-Checking
Despite its value, fact-checking faces challenges. Political parties often reject corrections and accuse fact-checkers of bias. In polarized environments, some voters dismiss fact-checking if it contradicts their preferred narrative. Fact-checkers must remain transparent in their methods, clearly explain evidence, and maintain independence from political influence to preserve credibility.
How to Do Fact-Checking in Politics
Fact-checking in politics involves systematically verifying claims made by politicians, parties, and campaigns. This process requires gathering reliable evidence, consulting primary sources such as government records and official data, and cross-checking with independent research. Journalists, fact-checking organizations, and even AI tools assess the accuracy of speeches, debates, advertisements, and social media posts. By using transparent methods and citing credible references, fact-checking helps expose falsehoods, challenge misleading narratives, and give voters trustworthy information to make informed decisions.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Identify the Claim | Start by isolating the specific political statement, promise, or statistic that needs verification. |
| Gather Reliable Sources | Consult primary sources such as government records, official reports, and verified data sets. |
| Cross-Check Evidence | Compare the claim with multiple independent and credible references to confirm consistency. |
| Use Fact-Checking Tools | Leverage fact-checking platforms, AI tools, and databases to quickly validate or disprove statements. |
| Assess Context | Examine whether the claim has been presented accurately, selectively, or out of context. |
| Publish Findings Transparently | Present results with clear evidence, citations, and explanations so voters can judge credibility. |
Why Are Fact-Checking Platforms Important for Democratic Accountability
Fact-checking platforms play a crucial role in promoting democratic accountability by verifying the accuracy of political claims and ensuring transparency in public discourse. By reviewing speeches, campaign promises, advertisements, and policy statements, these platforms expose false or misleading information that can distort voter perception. They hold leaders accountable for their words and actions, reduce the spread of disinformation, and provide you with access to reliable information needed to make informed choices. This process strengthens trust in democratic systems by promoting honesty and integrity in political communication.
Strengthening Transparency in Public Discourse
Fact-checking platforms strengthen transparency by verifying the accuracy of political claims. Politicians often make bold statements about economic performance, welfare benefits, or government achievements. Without verification, these claims can distort public perception. Fact-checking platforms review speeches, campaign ads, and policy documents, then publish clear assessments. This process enables you to distinguish between truth, exaggeration, and falsehood.
Holding Leaders Responsible
Democratic systems depend on leaders being accountable to the public. Fact-checking platforms create that accountability by tracking and exposing false statements. When leaders know their claims will be examined, they are more likely to rely on accurate information. For voters, this means you can trust that misleading rhetoric has a counterbalance.
Reducing the Spread of Disinformation
False political narratives spread quickly, especially on social media. Fact-checking platforms identify misleading posts, videos, or advertisements and provide corrections to ensure accuracy. By doing so, they limit the reach of misinformation campaigns that aim to influence your opinion. The presence of fact-checking discourages the use of deceptive strategies in elections and policy debates.
Supporting Informed Decision-Making
A functioning democracy requires voters to make decisions based on facts. Fact-checking platforms provide the verified information you need to assess candidates, policies, and party positions. Instead of relying on campaign rhetoric alone, you gain access to evidence-based analysis that helps you vote with confidence.
Building Trust in Democratic Processes
Trust in democratic systems erodes when misinformation dominates public discussion. Fact-checking platforms restore confidence by demonstrating the existence of independent verification. When you know that claims undergo scrutiny, you are less likely to feel manipulated. This trust reinforces participation and strengthens democratic values.
Challenges and the Need for Independence
Fact-checking platforms face accusations of bias, especially when their findings challenge powerful political groups. To remain effective, they must be independent, transparent in their methodology, and consistent in their evaluations. Clear communication of how claims are verified is essential for earning public trust.
How Can AI Fact-Checkers Reduce Political Disinformation Online
AI fact-checkers reduce political disinformation online by quickly analyzing large volumes of content across social media, news outlets, and digital campaigns. They detect misleading claims, manipulated images, and deepfake videos using machine learning and natural language processing. By automating the identification of false narratives, AI fact-checkers provide faster corrections and help prevent misinformation from spreading widely. This technology strengthens the accuracy of political communication, protects voters from manipulation, and supports more informed democratic participation.
Speed and Scale in Detecting False Claims
AI fact-checkers process information faster than human reviewers. They scan speeches, press releases, and social media posts to flag statements that require verification. By analyzing large volumes of content in real time, AI reduces the delay between a false claim being made and the correction being published. This speed prevents misinformation from spreading unchecked and reaching voters before corrections can be made.
Identifying Manipulated Media
Political disinformation is not limited to text. Deepfakes, altered images, and edited videos are increasingly used as standard tools to mislead the public. AI models trained in computer vision can detect inconsistencies in audio and video files, identifying manipulations that human eyes may miss. This ability protects you from being influenced by fabricated content that appears authentic.
Tracking Patterns of Disinformation
Disinformation often follows recognizable patterns, such as repeated use of specific narratives or coordinated sharing by networks of accounts. AI fact-checkers utilize machine learning to identify and track these patterns across various platforms. By mapping how false claims spread, they reveal organized campaigns and allow quicker intervention. This insight helps you see not just the falsehood itself but also the strategy behind it.
Supporting Human Reviewers
While AI excels at detection, human judgment is essential for context. Fact-checking platforms combine automated tools with editorial teams that evaluate evidence and assign ratings of truthfulness. AI provides efficiency, and humans provide reasoning. Together, they ensure that corrections are accurate, fair, and transparent.
Improving Public Awareness
AI fact-checkers also help make verified information more visible. Once a claim is rated as false or misleading, platforms can highlight the correction across search results, news feeds, and recommendation systems. This reduces the reach of disinformation while giving you access to fact-based updates that counter false narratives.
Challenges in AI Fact-Checking
AI fact-checkers face challenges, such as biased training data and attempts by disinformation groups to evade detection. Accuracy depends on continuous updates and transparency in how algorithms work. To maintain public trust, fact-checking platforms must clearly explain how AI reaches its conclusions and avoid opaque decision-making processes.
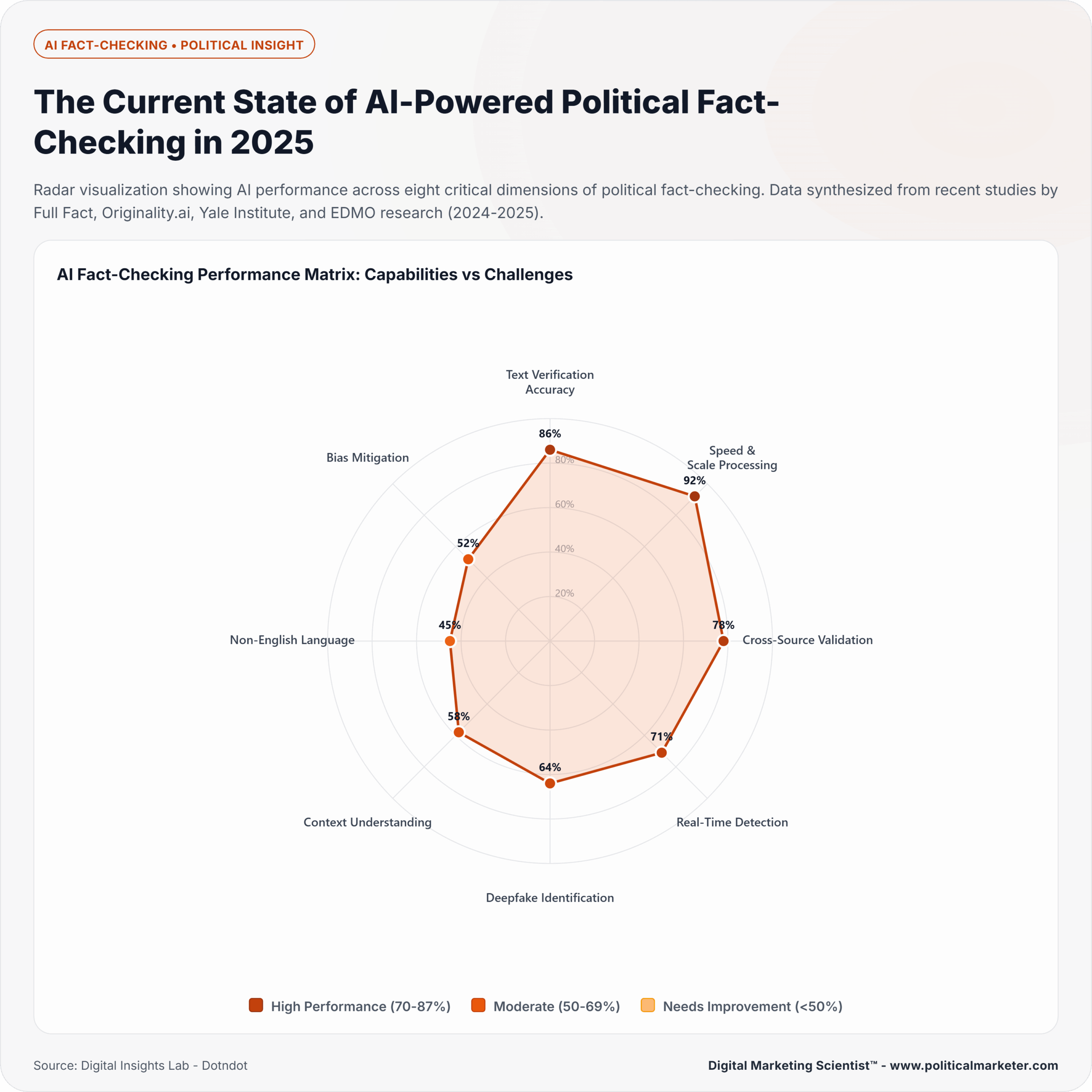
What Are the Biggest Challenges in Fact-Checking Political Speeches
The biggest challenges in fact-checking political speeches include the sheer volume of claims made in a short time, the use of vague or emotionally charged language, and limited access to reliable data for immediate verification. Politicians often frame statements in ways that blend truth with exaggeration, making them more challenging to assess quickly. Real-time corrections also struggle to keep pace with live speeches, where misinformation can spread before fact-checkers respond. These obstacles make the process complex but highlight why independent verification remains essential for keeping political communication accountable.
High Volume of Claims
Political speeches often include dozens of claims within a short timeframe. Fact-checkers must process and verify each statement against credible data, official reports, and historical records to ensure accuracy. The speed and volume make it difficult to provide immediate corrections, especially during live events where misinformation spreads before accurate analysis is available.
Ambiguity and Vague Language
Politicians often employ ambiguous language, selectively use statistics, or make broad generalizations. Statements framed in this way are more challenging to assess because they avoid precise facts that can be verified directly. For example, a claim that the economy is “stronger than ever” lacks measurable benchmarks, leaving fact-checkers with limited grounds for a clear verdict.
Access to Reliable Data
Fact-checkers need timely and accurate data to evaluate claims. In some cases, official information is incomplete, outdated, or not publicly available. When reliable sources are limited, fact-checkers face delays in producing assessments. This gap allows false or misleading statements to gain traction before corrections are published.
Real-Time Verification Limits
During live speeches or debates, fact-checkers work under intense pressure. They must verify statements while the audience is actively listening and forming opinions. The pace of delivery leaves little time to thoroughly analyze each claim. As a result, real-time corrections often focus only on the most significant or clearly false statements, while others go unchecked in the moment.
Risk of Perceived Bias
When fact-checkers label a statement as false or misleading, political supporters often accuse them of bias. This undermines trust, even if the analysis is accurate and evidence-based. The challenge is not only to fact-check correctly but also to communicate findings transparently so the public understands how conclusions were reached.
Complex Policy Issues
Some political speeches address complex topics, such as healthcare reform, tax policy, or international trade. These areas require specialized knowledge and detailed analysis. Fact-checkers must simplify explanations for the public without losing accuracy, which is difficult when policies involve technical or legal details.
Speed of Misinformation Spread
Even when fact-checkers publish corrections, misinformation often circulates more quickly and reaches a larger audience. Social media algorithms amplify attention-grabbing claims, while corrections usually receive less visibility. This imbalance reduces the effectiveness of fact-checking in stopping false narratives once they are widely shared.
How Do Fact-Checking Organizations Verify Government Policy Claims
Fact-checking organizations verify government policy claims by comparing official statements with evidence from credible sources such as government reports, budget documents, legislation, and independent research. They analyze whether the claim matches recorded data, evaluate the context in which it was made, and consult subject experts when policies involve technical or specialized knowledge. By breaking down complex information into clear, evidence-based findings, fact-checkers help you understand whether government policies are accurately represented or mischaracterized in political communication.
Reviewing Official Documents
Fact-checking organizations start by examining government-issued documents. These include policy papers, budget records, parliamentary proceedings, and legislative texts. By comparing a politician’s statement with what is written in these records, fact-checkers determine whether the claim reflects the actual policy. This method ensures that the analysis is grounded in verifiable evidence rather than opinion.
Consulting Independent Data Sources
Government claims are not always self-contained, so fact-checkers cross-check them with independent data. They may review reports from oversight bodies, academic research, economic surveys, and international organizations. This step provides a broader perspective, confirming whether a claim is consistent with external evidence. For example, a statement about job creation would be compared against labor market surveys and census data.
Analyzing Context and Scope
Politicians often make selective claims, highlighting favorable outcomes while ignoring limitations. Fact-checkers assess the broader context of the policy to avoid misleading impressions. If a leader claims that a new health program covers “all citizens,” fact-checkers examine eligibility rules, funding provisions, and implementation data to reveal who actually benefits. This prevents distortion of facts through selective framing.
Consulting Experts
Complex policy areas, such as taxation, healthcare, or environmental regulation, require subject expertise. Fact-checkers consult economists, legal analysts, or domain specialists to interpret technical language and clarify how the policy works in practice. This step ensures accuracy when claims involve specialized knowledge that the general public may not fully understand.
Tracking Implementation
Verifying policy claims also involves checking implementation data. Governments may announce ambitious programs, but their implementation often lags. Fact-checkers compare official promises with actual outcomes, such as progress reports, audits, or ground-level evidence. This distinction between intent and results helps you understand whether the policy has achieved what leaders claim.
Challenges in Verification
Fact-checking policy claims is complex because governments sometimes withhold data or release partial information. Political leaders also use ambiguous wording that allows multiple interpretations. These factors delay verification and create space for misinformation. To maintain credibility, fact-checking organizations must clearly communicate these limitations and explain how they arrived at their conclusions.
Why Is Real-Time Fact-Checking Critical During Political Debates
Real-time fact-checking is crucial during political debates because it immediately verifies claims made on stage before misinformation can shape public opinion. Politicians often use statistics, records, or policy references to strengthen their arguments, and false or misleading statements can influence millions of viewers in seconds. By providing instant corrections and context, real-time fact-checking helps you separate Fact from exaggeration, reduces the impact of false claims, and ensures that debates remain grounded in evidence rather than rhetoric.
Immediate Verification of Claims
During debates, politicians often present statistics, past achievements, or promises designed to influence voters. Real-time fact-checking verifies these claims as the discussion unfolds, reducing the risk that false information influences public opinion. By responding instantly, fact-checkers prevent misinformation from spreading unchecked across live broadcasts and social media.
Countering the Speed of Misinformation
False statements gain traction quickly in televised debates and online commentary. A misleading claim can reach millions before fact-checkers publish traditional reports. Real-time checks counter this speed by providing corrections immediately, ensuring that audiences are not left with unchallenged falsehoods.
Supporting Voter Judgment
Debates are moments when many voters form or revise their opinions about candidates. Real-time fact-checking gives you accurate context to assess performance on the spot. Instead of relying on rhetoric, you can judge candidates on the truthfulness of their claims and the strength of their arguments.
Reducing Strategic Manipulation
Some politicians deliberately use exaggeration or misleading statistics, knowing that corrections usually come later. Real-time fact-checking changes this dynamic by removing the advantage of spreading falsehoods in front of a live audience. It forces candidates to rely on accurate statements or risk immediate exposure.
Building Trust in the Debate Process
When fact-checking is visible and accessible during a debate, it strengthens trust in the democratic process. You can watch corrections unfold alongside the speeches, which creates accountability and encourages more evidence-based discussion. This transparency helps ensure that debates inform voters rather than mislead them.
Challenges in Real-Time Fact-Checking
Despite its importance, real-time fact-checking is a challenging task. Debates move quickly, claims are complex, and reliable data is not always immediately available. Fact-checkers must prioritize the most significant or potentially misleading statements, which means some claims remain unchecked until after the event. Clear communication about what is verified in real-time and what requires further review is essential for maintaining accuracy.
How Effective Is Fact-Checking in Countering Viral Fake News
Fact-checking is effective in countering viral fake news by identifying false claims, providing verified information, and limiting the reach of misinformation. While fake news often spreads faster than corrections, fact-checking helps reduce its long-term influence by offering evidence-based clarity. It equips you with reliable context to evaluate political content and discourages the deliberate use of false narratives in campaigns. Although not every false claim can be stopped immediately, consistent fact-checking improves public awareness and strengthens democratic accountability.
Identifying and Correcting False Claims
Fact-checking is effective in identifying viral fake news by systematically reviewing political statements, social media posts, and campaign advertisements. Fact-checkers compare these claims against verifiable evidence such as government records, independent research, and expert analysis. Once a false claim is confirmed, they publish corrections that provide clear context and explain why the claim is misleading or untrue.
Limiting the Influence of Disinformation
Fake news often spreads faster than factual reporting because it is designed to provoke strong reactions. While fact-checking cannot prevent the initial spread, it reduces the long-term influence by making accurate information more accessible. When platforms integrate fact-checking results into feeds and search engines, false claims lose visibility, and voters see corrections alongside the misinformation.
Educating the Public
Fact-checking does more than issue corrections. It teaches you how to critically evaluate political information. By showing the sources and methods used to verify claims, fact-checkers give you tools to recognize patterns of manipulation. This educational role strengthens public resilience against repeat exposure to false narratives.
Building Accountability for Politicians
The presence of fact-checking also discourages politicians and campaign teams from relying on false or exaggerated claims. Knowing that their statements will be verified in real-time makes leaders more cautious about presenting evidence. This pressure contributes to a more honest and accountable political environment.
Challenges in Effectiveness
Fact-checking faces challenges when combating viral fake news. False claims often reach millions before corrections are published. Some voters dismiss fact-checks if they conflict with political loyalties. Disinformation campaigns also adapt, utilizing new formats, such as memes or deepfakes, to bypass detection. Despite these challenges, continuous exposure to verified information reduces the credibility of repeated falsehoods over time.
What Tools Help Journalists Fact-Check Political Advertisements Quickly
Journalists employ a range of tools to quickly fact-check political advertisements, including databases of government records, campaign finance reports, and public policy archives. Digital verification tools, such as reverse image search, video forensics, and metadata analysis, help identify manipulated visuals or misleading edits in advertisements. Natural language processing software and AI-powered platforms scan ad scripts for false claims and match them against credible data sources. These tools allow journalists to respond rapidly, ensuring that political advertising is transparent and voters receive accurate information.
Accessing Public Records and Databases
Journalists often rely on official databases to verify claims in political ads. These include government archives, budget documents, campaign finance reports, and legislative records. By cross-checking ad content with these sources, they confirm whether a claim is supported by official evidence or misrepresented.
Digital Verification Tools
Visual elements in political ads are frequently manipulated. To detect edits or fabrications, journalists use tools such as reverse image searches, metadata analysis, and video forensics. These tools help confirm whether footage is authentic, altered, or taken out of context. They are handy for ads that rely on emotional imagery or misleading visuals.
AI and Natural Language Processing
AI-powered tools scan ad scripts and identify statements that require verification. Natural language processing compares ad content against existing datasets, including news archives and fact-checking databases, to identify relevant information. This technology accelerates the process of identifying inaccuracies and reduces the time required for manual review.
Social Media Monitoring
Many political ads circulate first on social platforms before reaching traditional media. Journalists use monitoring tools to track how ads spread, who is amplifying them, and whether coordinated campaigns are involved. This information helps them understand both the content and the strategy behind disinformation.
Collaboration With Fact-Checking Platforms
Journalists frequently collaborate with dedicated fact-checking organizations. Shared databases and cross-platform partnerships provide access to prior verifications, making it easier to confirm or debunk recurring claims. This collaboration ensures consistency in addressing misleading content across outlets.
Challenges in Rapid Verification
While these tools are practical, journalists face challenges such as limited access to real-time data, the speed of ad distribution, and the volume of content they must manage. Political advertisers release ads quickly and often across multiple platforms, which forces journalists to prioritize the most impactful or misleading claims for immediate review.
How Can Voters Identify Credible Fact-Checking Sources During Elections
Voters can identify credible fact-checking sources during elections by looking for transparency, independence, and evidence-based reporting. Reliable platforms clearly explain their methods, cite original data, and avoid partisan influence. They publish corrections when errors occur and show how conclusions are reached. By verifying whether a fact-checking organization is recognized by reputable networks, such as the International Fact-Checking Network (IFCN), and cross-referencing claims across multiple trusted outlets, you can ensure that the information you rely on is accurate and unbiased.
Look for Transparency in Methods
Credible fact-checking sources clearly explain how they arrive at their conclusions. They cite original data, provide links to reports, and describe their verification process. When you see a transparent breakdown of evidence, you can judge for yourself whether their findings are reliable.
Check for Independence
Fact-checking organizations must remain free from political or corporate influence. If a platform shows bias toward a particular party or fails to fact-check certain groups, its credibility is weakened. Reliable sources apply the same standards to all political actors, regardless of affiliation.
Review Evidence and Citations
A credible source always backs up its claims with verifiable data. Look for references to government records, independent studies, or expert opinions. If a fact-check relies only on opinion without supporting evidence, it is less trustworthy.
See if They Correct Errors
Even the best fact-checking platforms make mistakes. What sets credible ones apart is their willingness to correct errors publicly. Check whether the organization has a correction policy and how it handles revisions. This practice shows accountability and strengthens trust.
Recognize Established Standards
Some fact-checking organizations adhere to recognized codes of practice, such as those established by the International Fact-Checking Network (IFCN). Membership in these networks requires compliance with standards on transparency, fairness, and accountability. If a platform meets these standards, you can consider it more reliable.
Compare Across Multiple Sources
One fact-check alone may not provide the complete picture. Cross-referencing claims across different trusted outlets helps you confirm consistency. When multiple independent organizations verify the same claim, you can have greater confidence in the accuracy of the information.
Why Do Political Parties Dispute Independent Fact-Checking Reports
Political parties dispute independent fact-checking reports because unfavorable findings can damage their credibility and weaken their campaigns. Parties often claim bias when reports challenge their statements, framing fact-checkers as aligned with opponents. In highly polarized environments, supporters may reject corrections that contradict party narratives. These disputes are less about evidence and more about political strategy, as questioning fact-checking helps parties protect their image, control narratives, and maintain influence over their voter base.
Protecting Political Image
Political parties dispute independent fact-checking reports because unfavorable findings damage their public image. When fact-checkers label a statement false or misleading, it undermines the credibility of leaders and weakens campaign narratives. To avoid reputational harm, parties often challenge these reports instead of accepting the corrections.
Claiming Bias and Partisanship
A typical response is to accuse fact-checkers of political bias. Parties argue that corrections favor opponents or selectively target their side. By framing fact-checking organizations as partisan, they shift the focus from the accuracy of the claim to the supposed motives of the reviewers. This strategy helps them rally supporters while deflecting from the evidence.
Managing Polarized Support Bases
In highly polarized environments, supporters often reject information that contradicts their party’s narrative. Parties dispute fact-checks to reinforce loyalty, signaling to their base that outside criticism is untrustworthy. This behavior strengthens group identity but reduces space for evidence-based debate.
Controlling the Narrative
Fact-checking disrupts the ability of parties to frame issues on their own terms. When corrections circulate widely, they challenge campaign messaging and reduce the effectiveness of ads, speeches, or social media strategies. By disputing fact-checking, parties attempt to maintain control over how voters interpret information.
Undermining Independent Watchdogs
Some disputes aim to erode public trust in independent fact-checkers. If voters come to believe that these organizations are unreliable, the corrective impact of fact-checking is reduced. This benefits parties that frequently rely on exaggeration or misleading claims.
What Methods Are Used to Fact-Check Social Media Posts in Politics
Fact-checking social media posts in politics involves verifying claims through multiple methods, including cross-checking with official records, news archives, and independent research. Analysts use reverse image search, video forensics, and metadata analysis to identify manipulated visuals or misleading edits. AI tools and natural language processing scan posts for false narratives and compare them against verified databases. Fact-checkers also monitor coordinated sharing patterns to detect organized disinformation campaigns. By combining technology with expert review, these methods ensure that political content shared online is accurately assessed and corrected.
Cross-Checking With Reliable Records
Fact-checkers verify claims in political posts by comparing them with credible sources such as government records, election data, and official policy documents. They also review reputable news archives and independent research to confirm whether statements are accurate or misleading. This ensures that claims are judged against verifiable evidence rather than opinion.
Image and Video Verification
Political disinformation often relies on manipulated visuals. Fact-checkers use reverse image search, metadata analysis, and video forensics to confirm authenticity. These tools reveal whether a photo has been taken out of context, digitally altered, or recycled from unrelated events. Identifying such manipulation prevents misleading images from influencing public perception.
AI-Powered Detection
Artificial intelligence and natural language processing tools scan social media posts for false narratives, recurring themes, and exaggerated claims. These systems compare text and video content against verified databases and flag suspicious material. This automation enables fact-checkers to process high volumes of content at the speed necessary to keep pace with viral posts.
Monitoring Disinformation Networks
Fact-checkers track how posts spread across platforms. By analyzing sharing patterns and identifying coordinated activity, they uncover organized campaigns designed to amplify false narratives. This method helps expose the strategy behind disinformation, not just the content itself.
Expert Consultation
Some claims involve specialized knowledge, such as economic policy or public health. In these cases, fact-checkers consult subject experts to interpret technical details and ensure accuracy. Expert input enhances credibility and facilitates the explanation of complex issues to the public in simpler terms.
Public Corrections and Transparency
Once a claim is verified, organizations publish corrections that include clear explanations of their methods and sources. They also disclose any limitations when complete data is not available. This transparency helps build trust and ensures that voters understand how conclusions were reached.
Challenges in Verification
Social media posts spread faster than fact-checks can be produced. False information often reaches millions before corrections circulate. Another challenge is public skepticism, as some users dismiss fact-checks that conflict with their political beliefs. Despite these obstacles, combining technology, expert analysis, and transparent reporting makes fact-checking an essential tool in protecting voters from online manipulation.
How Does Fact-Checking Influence Public Trust in Politicians
Fact-checking influences public trust in politicians by holding leaders accountable for their statements and exposing false or exaggerated claims. When voters see consistent verification backed by evidence, they are more likely to trust politicians who make accurate statements and question those who spread misinformation. However, in polarized environments, some supporters dismiss fact-checks that challenge their party, which limits their impact. Overall, fact-checking strengthens democratic accountability by promoting honesty and encouraging politicians to rely on verified information.
Holding Politicians Accountable
Fact-checking holds politicians accountable by exposing false or exaggerated claims. When independent organizations verify statements against reliable data, they make it harder for leaders to mislead the public. This accountability builds confidence among voters who value evidence over rhetoric.
Rewarding Accuracy
Politicians who consistently make truthful statements benefit from fact-checking. When their claims are verified as accurate, it reinforces credibility and strengthens their reputation. Voters are more likely to trust leaders who can demonstrate reliability through independent verification.
Reducing the Impact of Falsehoods
Fact-checking limits the effect of misinformation in campaigns and policy debates. By quickly addressing inaccurate claims, fact-checkers reduce the likelihood that falsehoods shape long-term voter perception. This process helps maintain an informed electorate, which is central to democratic trust.
Challenges in Polarized Environments
In polarized political contexts, fact-checking can have limited impact. Supporters sometimes reject corrections that contradict their party’s narrative. Instead of reducing trust in dishonest politicians, fact-checks may deepen divides if they are perceived as partisan attacks. This highlights the difficulty of influencing public opinion when loyalty outweighs evidence.
Building Public Confidence in Democracy
Despite these challenges, fact-checking plays a crucial role in fostering overall trust in political systems. Transparent verification processes demonstrate that public debate is subject to scrutiny. This oversight ensures that voters are aware of accountability mechanisms, even if not all individuals accept them.
Fact-Checking AI: Should Independent Agencies Get Legal Mandates in Elections
The idea of giving independent agencies a legal mandate to use AI for fact-checking in elections raises essential questions about accountability and transparency. On one hand, legally empowered fact-checking can ensure faster detection of false claims, prevent disinformation from influencing voters, and standardize practices across platforms. On the other hand, it risks political pushback, accusations of bias, and concerns over government overreach if not implemented with clear safeguards in place. For voters, such mandates could provide stronger protection against misinformation; however, they must strike a balance between technological efficiency and independence, fairness, and public trust.
The Case for Legal Mandates
Independent fact-checking agencies supported by AI could play a decisive role in elections. A legal mandate would give them authority to verify claims made in speeches, advertisements, and social media campaigns. This would ensure faster corrections, reduce the influence of misinformation, and set consistent standards for all political actors. By embedding such agencies in the electoral framework, governments could create a more accountable and transparent environment for voters.
Advantages of AI Integration
AI tools can scan high volumes of content in real time, detect patterns in disinformation, and flag manipulated images or videos. When combined with independent oversight, these tools increase speed and accuracy in election fact-checking. This integration enables voters to access verified information promptly, thereby reducing the impact of false narratives before they gain traction.
Risks and Concerns
Mandating fact-checking through law raises concerns about political interference and accusations of bias. Parties that face unfavorable findings may argue that fact-checkers are unfair or politically motivated. There is also a risk that legal mandates, if not carefully designed, could restrict freedom of expression or concentrate too much power in a single authority. To maintain legitimacy, independent agencies must remain transparent, publish methodologies, and apply the same standards to all sides.
Balancing Independence and Regulation
For legal mandates to succeed, fact-checking agencies must operate independently from governments and political parties. Oversight could be provided by a multi-stakeholder body that includes journalists, academics, civil society groups, and technology experts. Clear safeguards would prevent misuse and protect the credibility of both AI systems and the agencies that use them.
Impact on Voters and Elections
A legal framework for AI-driven fact-checking would give voters more confidence that they are receiving accurate information during campaigns. It would discourage political actors from spreading falsehoods and make electoral debates more evidence-based. However, without strong safeguards, mandates risk being viewed as censorship, which could undermine public trust instead of strengthening it.
What Are Examples of Successful Fact-Checking Initiatives Worldwide
Several successful fact-checking initiatives worldwide have strengthened political accountability and helped counter misinformation. PolitiFact in the United States uses a “Truth-O-Meter” to rate political claims. At the same time, Full Fact in the United Kingdom provides real-time checks during debates and publishes detailed policy analyses. In India, Alt News and BOOM investigate viral political content on social media. Africa Check operates across multiple African countries, verifying government and campaign claims with data-driven reports. These initiatives demonstrate how independent organizations, often supported by technology and collaboration with media outlets, play a vital role in ensuring voters have access to accurate and verified political information.
Fact-checking initiatives worldwide play a crucial role in strengthening democratic processes, promoting accountability, and combating the spread of misinformation. These organizations operate independently, rely on transparent methods, and often collaborate with media, technology platforms, and civil society. By verifying political claims, policy statements, and viral content, they provide voters with reliable information to make informed decisions.
United States: PolitiFact
PolitiFact is one of the most recognized fact-checking organizations in the United States. It evaluates political claims using its “Truth-O-Meter,” which categorizes statements from “True” to “False.” The platform became well-known for holding elected officials, candidates, and public figures accountable during election campaigns. Its systematic approach and clear communication style made fact-checking accessible to a broad audience.
United Kingdom: Full Fact
Full Fact operates as an independent fact-checking charity in the UK. It monitors speeches, debates, and campaign materials, providing real-time corrections when misinformation spreads. The organization also collaborates with journalists and uses automated tools to scale fact-checking during elections. By publishing its methodology and sources, it builds credibility and public trust.
India: Alt News and BOOM
In India, where misinformation often spreads rapidly on social media, platforms like Alt News and BOOM specialize in verifying viral claims and political content. They use open-source tools, digital forensics, and crowd-sourced reporting to debunk manipulated images, videos, and false narratives. Their work has been crucial in addressing communal misinformation and politically charged propaganda.
Africa: Africa Check
Africa Check operates across multiple countries, including South Africa, Nigeria, and Kenya. It focuses on verifying claims made by politicians, public figures, and the media. The organization publishes evidence-based reports, often supported by data from government records and international research. By targeting health, education, and governance-related misinformation, Africa Check strengthens public accountability in developing democracies.
Global Collaborations: IFCN and Media Partnerships
The International Fact-Checking Network (IFCN) sets ethical and methodological standards for fact-checkers globally. Many organizations join the IFCN Code of Principles, which promotes transparency, non-partisanship, and accountability. In addition, partnerships with social media platforms such as Facebook and Google have expanded the reach of independent fact-checking, allowing corrections to appear directly alongside misleading posts.
Key Lessons from Global Initiatives
Successful fact-checking efforts share common traits: independence, transparency, use of technology, and strong collaboration with media and civic organizations. These initiatives demonstrate that fact-checking is most effective when it operates openly, avoids political bias, and communicates its findings in a clear and accessible format.
Why Should Citizens Rely on Fact-Checking Before Voting
Citizens should rely on fact-checking before voting because it helps separate verified information from false or misleading claims. Fact-checking enables voters to assess political promises, policy statements, and campaign advertisements with clarity and confidence, based on evidence. By depending on credible sources, citizens reduce the risk of being misled by propaganda or viral misinformation. This process empowers them to make informed choices, strengthens democratic accountability, and ensures that their vote reflects reality rather than distortion.
Elections determine who governs and how policies shape people’s lives. Campaigns often involve bold promises, emotional appeals, and in many cases, misleading claims. Citizens who want to vote responsibly need accurate information. Fact-checking provides this by separating truth from distortion, allowing voters to base their decisions on verified evidence rather than propaganda.
Filtering Misinformation
Political campaigns often include exaggerated statistics, selective data use, or outright falsehoods. Social media exacerbates this problem by disseminating unverified content rapidly. Fact-checking helps filter this noise by reviewing claims against credible data sources. When voters use verified information, they are less likely to be misled by sensational headlines or manipulated narratives.
Strengthening Accountability
Fact-checking ensures that politicians know their words will be scrutinized. When independent organizations verify campaign promises and public statements, it creates a record of accuracy and transparency. This not only exposes false claims but also encourages leaders to speak more responsibly. For citizens, this accountability mechanism builds trust in the political process.
Supporting Informed Decision-Making
Casting a vote is one of the most significant civic actions. To make informed choices, citizens must understand which policies are realistic and which are designed to mislead. Fact-checking provides clarity by testing claims against reliable evidence, whether those claims come from manifestos, debates, or advertisements. By doing so, it empowers citizens to align their votes with facts rather than political spin.
Reducing Polarization
Misinformation often thrives in polarized environments, where partisanship clouds judgment. Fact-checking introduces evidence into the discussion, helping reduce the influence of emotional or biased narratives. While not all voters will accept corrections, access to verified facts helps moderate debates and gives undecided or skeptical voters a clearer picture.
Building Trust in Democracy
Trust in the democratic process relies on transparency and fairness. When voters believe they have access to accurate information, they are more likely to participate actively and view outcomes as legitimate. Fact-checking supports this by ensuring that unchecked falsehoods do not dominate campaigns.
How Do Algorithms Assist in Political Fact-Checking at Scale
Algorithms assist political fact-checking at scale by automating the detection, analysis, and verification of claims made in speeches, debates, and social media posts. They scan large volumes of text, audio, and video to identify recurring statements, cross-check them against verified databases, and flag inconsistencies. Natural language processing helps interpret political language, while machine learning models detect patterns of misinformation. These tools accelerate the verification process, enable fact-checkers to cover more content in real-time, and reduce manual workload, making large-scale monitoring of political communication more efficient and accurate.
Fact-checking political claims at scale is a significant challenge due to the vast amount of speeches, debates, advertisements, and social media content produced daily. Algorithms play a key role in meeting this challenge by automating the detection and verification process. They allow fact-checkers to analyze large datasets quickly, identify misleading claims, and provide voters with timely corrections.
Automated Claim Detection
Natural language processing (NLP) models aid in detecting political claims within speeches, debates, and social media posts. These algorithms are trained to recognize statements that are factual in nature, such as statistics, policy promises, or references to past events. By filtering out opinion-based or rhetorical language, algorithms focus fact-checking resources on statements that can be verified with evidence.
Cross-Referencing with Databases
Once claims are identified, algorithms cross-check them against verified datasets, government records, historical archives, and previous fact-checks. For example, if a politician cites economic growth numbers, algorithms can quickly compare those claims with official government statistics. This process reduces manual research time and ensures more consistent verification.
Detecting Patterns of Misinformation
Machine learning models are designed to spot recurring false claims or coordinated disinformation campaigns. By analyzing how certain statements spread across platforms, algorithms help fact-checkers identify which narratives are being amplified. This enables the prioritization of verifying claims that have the broadest reach or the highest potential to mislead voters.
Real-Time Monitoring
During live debates and election events, algorithms assist in real-time fact-checking by transcribing speech, identifying key claims, and flagging them for immediate review. This enables fact-checkers to provide prompt responses and prevent false statements from influencing public opinion unchecked.
Visual and Multimedia Fact-Checking
Algorithms also support verification beyond text. Image recognition tools can detect manipulated photos or videos, while deepfake detection systems help identify synthetic media. These tools are essential as visual misinformation becomes more common in political campaigns.
Limitations and Human Oversight
Although algorithms improve speed and coverage, they cannot replace human judgment. Context, tone, and cultural nuances still require human interpretation. Effective fact-checking combines algorithmic efficiency with expert analysis to ensure accuracy and fairness.
What Is the Impact of Fact-Checking on Voter Behavior Studies
Research on voter behavior indicates that fact-checking affects how citizens process political information and make electoral decisions. Studies suggest that exposure to fact-checks reduces belief in false claims, increases awareness of misleading rhetoric, and encourages more critical evaluation of political messages. However, the impact varies: some voters adjust their views based on corrections, while highly partisan individuals often resist or dismiss fact-checks that challenge their preferred candidates. Overall, fact-checking has a measurable impact on reducing misinformation, shaping political perceptions, and promoting accountability in democratic participation.
Fact-checking plays a central role in shaping voter behavior because it provides an evidence-based counter to misinformation spread by politicians, campaigns, or social media. Studies on voter behavior show that fact-checking influences belief formation, voting intentions, and levels of trust in political actors. While its impact is not uniform across all groups, it has measurable effects on how voters process political information.
Reducing Belief in False Claims
Research consistently shows that fact-checking reduces belief in false or misleading claims. When voters are exposed to corrections accompanied by supporting data, they are less likely to cling to inaccurate information. This effect is most substantial among undecided or less partisan voters who are open to new evidence.
Shaping Voting Decisions
Fact-checking not only changes perceptions of specific claims but also influences voting decisions. Voters who see repeated corrections are more cautious about supporting candidates associated with misinformation. This creates indirect pressure on politicians to avoid making false statements, knowing that independent checks will expose them.
Influence of Partisanship
Partisan loyalty plays a significant role in how voters respond to fact-checks. Supporters of a candidate may dismiss corrections as biased, even when the evidence is clear and compelling. This resistance limits the reach of fact-checking among strongly polarized groups. However, studies show that independent or swing voters respond more positively, adjusting their views based on verified information.
Building Accountability and Trust
Fact-checking enhances political accountability by creating a public record of accuracy and transparency. Voters gain greater trust in the political process when they see false claims challenged with evidence. Over time, this can increase confidence in elections, reduce cynicism, and improve the quality of democratic debate.
Limitations in Impact
Fact-checking does not eliminate misinformation. Some false claims persist despite corrections, particularly when they are frequently repeated or shared within partisan echo chambers. Cognitive biases, such as motivated reasoning, also weaken the effect of corrections. These limitations underscore the need to integrate fact-checking with broader voter education and media literacy initiatives.
How Does Fact-Checking Help Combat Deepfakes in Politics
Fact-checking helps combat deepfakes in politics by verifying the authenticity of videos, images, and audio recordings that may be digitally manipulated to mislead voters. Fact-checkers use forensic tools, metadata analysis, and AI-based detection systems to identify signs of tampering. By publishing timely corrections and explanations, they prevent false narratives from spreading unchecked. This process not only exposes fabricated media but also educates the public on how to recognize and question manipulated content. In doing so, fact-checking reduces the influence of deepfakes on voter perception and safeguards democratic debate.
Deepfakes present one of the most serious threats to political communication. These manipulated videos, images, or audio recordings can misrepresent candidates, fabricate events, and mislead voters. Fact-checking plays a central role in countering this challenge by verifying authenticity, exposing manipulation, and educating citizens about how to identify false content.
Detecting Manipulated Media
Fact-checkers use digital forensic tools and AI-powered detection systems to analyze videos and images. They look for inconsistencies such as irregular shadows, mismatched lip movements, or altered audio. By combining technical analysis with metadata review and fact-checking, teams can confirm whether media has been manipulated or artificially generated.
Verification Through Trusted Sources
When a suspected deepfake circulates, fact-checkers verify the content by cross-checking it against original footage, official transcripts, and credible news archives. This ensures that claims attached to manipulated media are evaluated against verified records rather than speculation. The use of multiple independent sources enhances the credibility of the verification process.
Timely Corrections to Limit Spread
Deepfakes gain influence quickly when shared on social media. Fact-checking organizations counter this by issuing timely corrections, often accompanied by side-by-side comparisons of authentic and manipulated content. This rapid response helps prevent false narratives from dominating political discussions and reduces the likelihood that voters will be misled before making decisions.
Educating Voters on Media Literacy
Beyond debunking individual cases, fact-checking organizations play an educational role. They provide resources that teach voters how to question suspicious content, recognize signs of manipulation, and rely on verified sources. This proactive approach reduces long-term vulnerability to deepfake-driven misinformation.
Supporting Democratic Integrity
Unchecked deepfakes undermine trust in political communication and fuel cynicism about the democratic process. Fact-checking strengthens integrity by ensuring voters have access to accurate information. Exposing fabricated media discourages the use of deepfakes in campaigns and increases the political cost for actors who attempt to spread them.
Why Is Bipartisan Support Necessary for Political Fact-Checking Success
Bipartisan support is essential for the success of political fact-checking because it ensures that verification efforts are perceived as fair, impartial, and trustworthy. When fact-checking is backed or respected across party lines, voters are less likely to dismiss corrections as biased attacks. It reduces polarization, encourages broader acceptance of verified information, and strengthens accountability for all political actors. Without bipartisan recognition, fact-checking risks being viewed as partisan, which limits its effectiveness in shaping voter understanding and protecting democratic processes.
Fact-checking plays a crucial role in protecting democratic processes, but its effectiveness depends on the public’s trust. In polarized environments, voters often dismiss fact-checks that challenge their preferred candidates as biased. Bipartisan support helps counter this problem by lending legitimacy to fact-checking efforts across political divides.
Reducing Perceptions of Bias
One of the main challenges in political fact-checking is the perception that corrections favor one party over another. When fact-checking organizations are supported or acknowledged across party lines, it reduces accusations of partiality. This makes voters more likely to accept verified information as credible, regardless of political affiliation.
Encouraging Wider Acceptance
Without bipartisan recognition, fact-checking risks being ignored by segments of the electorate. Support from multiple parties ensures that corrections reach broader audiences and are not dismissed as partisan tools. This wider acceptance increases the overall effectiveness of fact-checking during campaigns and elections.
Promoting Political Accountability
Bipartisan support strengthens accountability by holding all parties to the same standards. When voters see that fact-checking applies equally to every political actor, it reduces selective criticism and encourages more honest communication. This levels the playing field and deters misinformation across the spectrum.
Building Public Trust
Trust in democratic systems depends on transparency and fairness. Fact-checking backed by bipartisan acknowledgment shows voters that verification is about truth, not political advantage. This helps restore confidence in public debate and reassures citizens that election outcomes reflect informed choices rather than misinformation.
How Can Educational Campaigns Improve Awareness of Political Fact-Checking
Educational campaigns improve awareness of political fact-checking by teaching citizens how to critically evaluate claims, recognize misinformation, and identify credible sources. By integrating fact-checking lessons into schools, universities, and community programs, these campaigns help voters understand how political narratives are constructed and how they can be corrected. Public awareness initiatives, workshops, and media literacy programs encourage people to question unverified information before sharing it. As a result, educational campaigns strengthen democratic participation by ensuring that citizens base their political choices on verified facts rather than misleading claims.
Educational campaigns play a critical role in equipping citizens with the skills needed to identify misinformation, verify claims, and make informed decisions during elections. By combining structured learning with practical tools, these campaigns help reduce the influence of false or misleading political content.
Building Media Literacy
Campaigns that focus on media literacy teach voters how to question sources, analyze political claims, and distinguish between factual reporting and opinion. This approach enables people to detect manipulation and resist misinformation.
Community and Institutional Outreach
Workshops, seminars, and training programs in schools, universities, and community centers increase awareness at multiple levels of society. When educators, civic organizations, and election bodies integrate fact-checking education, it reaches a broad audience and normalizes the practice of verifying information before accepting it as truth.
Collaboration with Media and Technology Platforms
Partnerships between fact-checkers, news outlets, and social media platforms enhance the visibility of fact-checking resources. Campaigns that utilize tools such as claim databases, reverse image search, and official election portals enable voters to verify content quickly.
Reducing the Spread of False Narratives
Educational campaigns encourage responsible online behavior by discouraging the sharing of unverified political content. When citizens understand the real-world impact of misinformation on democracy, they become less likely to spread false or misleading posts.
Strengthening Democratic Participation
Fact-checking awareness campaigns ultimately strengthen democracy by ensuring citizens make electoral choices based on verified information. Informed voters are better able to hold politicians accountable and challenge misleading narratives.
Conclusion
From the analyzed responses, it is clear that fact-checking plays a central role in maintaining the integrity of democratic processes. It ensures that citizens, journalists, and policymakers have access to accurate and verifiable information in a political environment where misinformation spreads rapidly, primarily through digital platforms.
Fact-checking improves public trust in politicians, influences voter behavior, and acts as a safeguard against fake news, deepfakes, and manipulative political advertisements. Independent and credible fact-checking organizations, supported by bipartisan recognition and transparency, are essential for legitimacy. AI and algorithms help scale fact-checking efforts, but human oversight remains vital to maintain accuracy and context.
Educational campaigns further strengthen awareness by teaching citizens how to verify claims, evaluate sources, and make informed decisions. However, challenges remain, such as political resistance, disputes over fact-checker credibility, and the speed at which false information spreads compared to the speed of verified corrections.
Fact-Checking in Politics: FAQs
What Is Political Fact-Checking?
Political fact-checking is the process of verifying claims made by politicians, parties, or interest groups to ensure accuracy and prevent the spread of misinformation.
How Does Fact-Checking Protect Voters From Misinformation?
It provides voters with accurate information, enabling them to make informed decisions rather than being influenced by false or misleading claims.
What Role Does Fact-Checking Play in Election Campaigns?
It holds candidates accountable, challenges false claims, and ensures that campaign narratives are based on verified facts.
Why Are Independent Fact-Checking Platforms Important for Democracy?
They provide non-partisan verification of political statements, strengthening accountability and reducing the risk of manipulation.
How Can AI-Powered Fact-Checkers Reduce Disinformation Online?
AI tools can detect patterns in misinformation, flag suspicious content, and cross-check political claims at scale with speed and consistency.
What Challenges Arise in Fact-Checking Political Speeches?
Issues include vague language, selective use of data, rapid speech delivery, and the immediate spread of soundbites without full context.
How Do Fact-Checking Organizations Verify Government Policy Claims?
They review official documents, cross-reference multiple data sources, consult experts, and compare policies with actual implementation.
Why Is Real-Time Fact-Checking Important During Political Debates?
It immediately challenges false claims, prevents misinformation from spreading unchecked, and helps voters understand the truth as they watch debates.
How Effective Is Fact-Checking in Countering Viral Fake News?
While not always able to stop the initial spread, fact-checking provides corrective information that reduces long-term belief in false stories.
What Tools Help Journalists Fact-Check Political Advertisements?
Journalists use reverse image search, deepfake detection software, data verification platforms, and archives of past campaign materials.
How Can Voters Identify Credible Fact-Checking Sources During Elections?
They should look for organizations with transparent methodologies, clear sourcing, bipartisan recognition, and international fact-checking certifications.
Why Do Political Parties Dispute Fact-Checking Reports?
Parties often reject fact-checks that challenge their narratives, labeling them biased or inaccurate, to maintain support from their base.
What Methods Are Used to Fact-Check Social Media Posts in Politics?
Fact-checkers use image forensics, metadata analysis, linguistic checks, AI-based pattern detection, and cross-verification with official sources.
How Does Fact-Checking Influence Public Trust in Politicians?
It exposes dishonesty, rewards accuracy, and shapes how citizens perceive a politician’s credibility over time.
Should Independent Fact-Checking Agencies Receive Legal Mandates During Elections?
Many experts argue that legal recognition would enhance authority, consistency, and accountability, though critics warn of risks to press freedom.
What Are Some Examples of Successful Fact-Checking Initiatives Worldwide?
PolitiFact (US), Full Fact (UK), Africa Check, and AltNews (India) are known for effectively challenging misinformation in their regions.
Why Should Citizens Rely on Fact-Checking Before Voting?
Fact-checking ensures that voters base their choices on evidence, not manipulation or false promises.
How Do Algorithms Assist in Political Fact-Checking at Scale?
Algorithms analyze large volumes of text, flag recurring falsehoods, and match claims against databases of verified facts, improving efficiency.
What Impact Does Fact-Checking Have on Voter Behavior?
Studies show that exposure to fact-checks reduces belief in false claims and can shift voter perceptions of candidate credibility.
How Does Fact-Checking Help Combat Deepfakes in Politics?
Fact-checkers use AI detection tools, video forensics, and source validation to expose manipulated media and prevent false narratives from spreading.